-
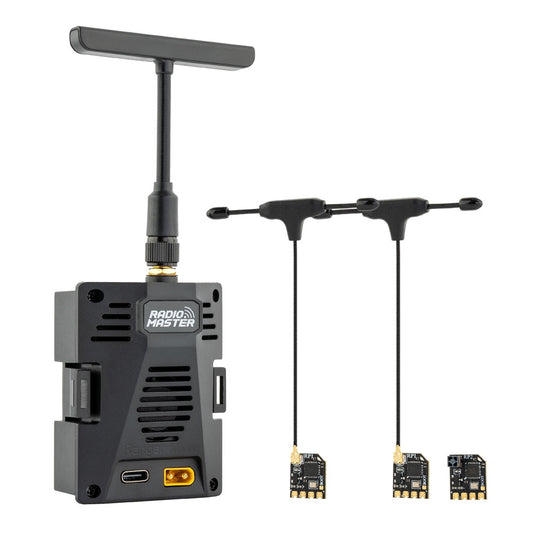
RadioMaster Ranger Micro 2.4GHz ELRS Module Combo Set for TX16S TX12 MKII
Regular price From $51.29 USDRegular priceUnit price per$76.94 USDSale price From $51.29 USDSale -
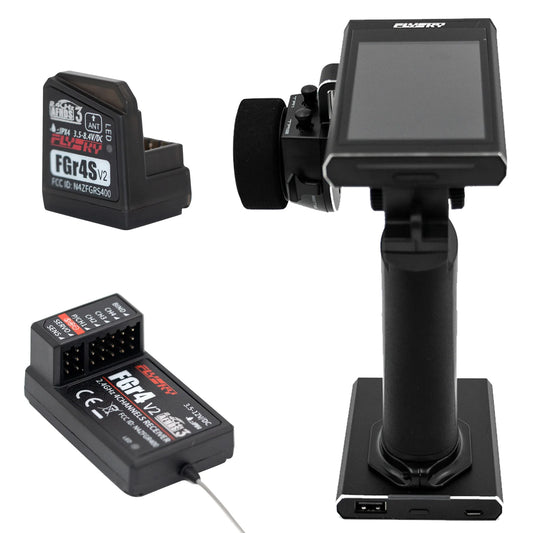
Flysky Noble NB4 2.4G 4CH Radio Transmitter - Remote Controller with FGR4 FGR4S Receiver AFHDS 3 Protocol for RC Car Boat Models
Regular price $346.21 USDRegular priceUnit price per$415.45 USDSale price $346.21 USDSale -
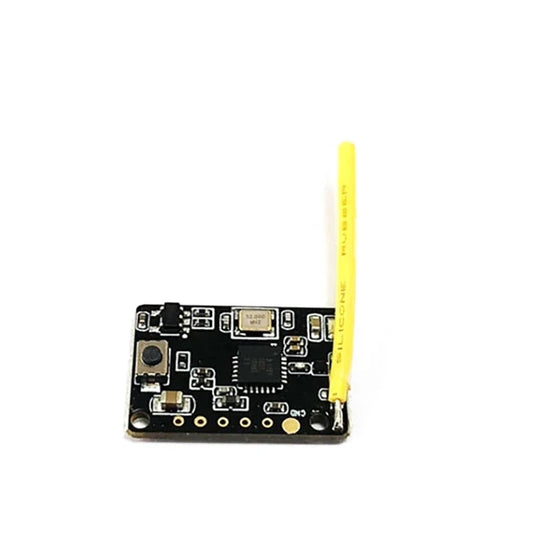
Flysky FS-MiniZRF3 2.4G Mini Receiver - Compatible for Flysky Noble NB4 For Mini-z EVO RC Car
Regular price $43.23 USDRegular priceUnit price per$56.20 USDSale price $43.23 USDSale -
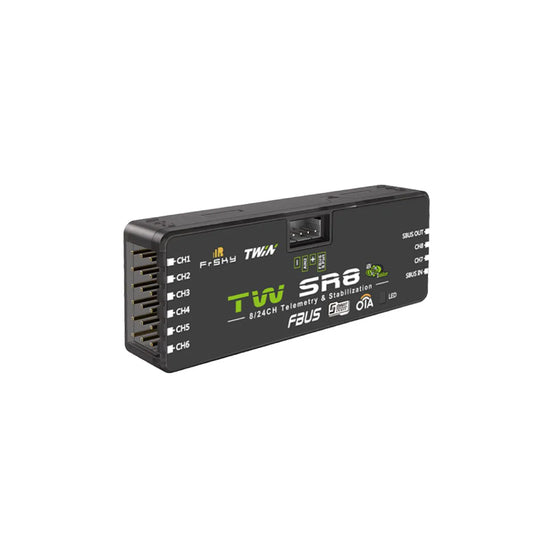
FrSky TW SR8 Receiver - TWIN Dual 2.4G Band ADV Stabilizer 8 PWM Channel Ports Long Control Range Drone Receiver
Regular price $99.98 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
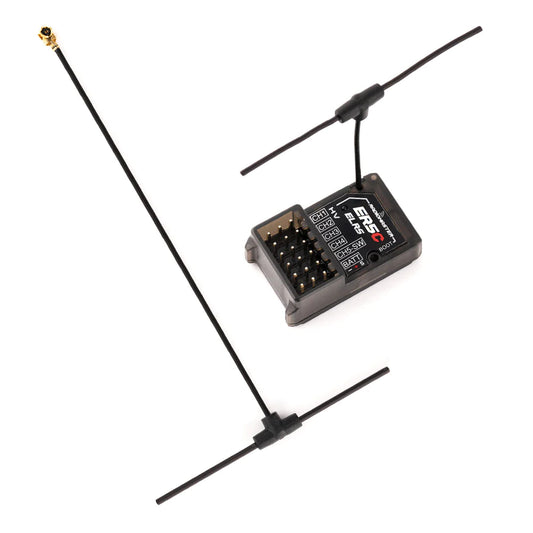
RadioMaster ER5C 2.4GHz 5Ch ELRS PWM Receiver - Supports 8.4V HV Servos Fit for Aircraft applications
Regular price $35.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
25W 60W Anti Drone Device - 1.5G 2.4G 5.8G 1KM Shielding Distance Detachable Portable Anti UAV Drone System
Regular price From $2,156.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
HappyModel ExpressLRS ELRS 2.4G RX SX1280 Nano Long Range Receiver PP EP1 EP2 RX EP1 TCXO/EP2 TCXO 10X10mm for RC Airplane
Regular price From $14.31 USDRegular priceUnit price per$28.62 USDSale price From $14.31 USDSale -
Jumper ELRS Aion Rx Mini 2.4GHZ 16CH Receiver Compatible with 2.4 mode 5KM Range Transmitter for RC Drone
Regular price $26.89 USDRegular priceUnit price per$40.62 USDSale price $26.89 USDSale -
CT210+CR800 TX RX Combo - 50KM Long Range 2.4GHz 2.4G FPV 1W 1000mw AV Wireless Transmission Telemetry Transmitter Receiver
Regular price $112.98 USDRegular priceUnit price per$169.46 USDSale price $112.98 USDSale -
Original TEAM BLACKSHEEP TBS Tracer Micro TX 2.4Ghz Radio System for RC Airplane FPV Racing Freestyle Drones FPV Remote Controller
Regular price $111.89 USDRegular priceUnit price per$167.83 USDSale price $111.89 USDSale -
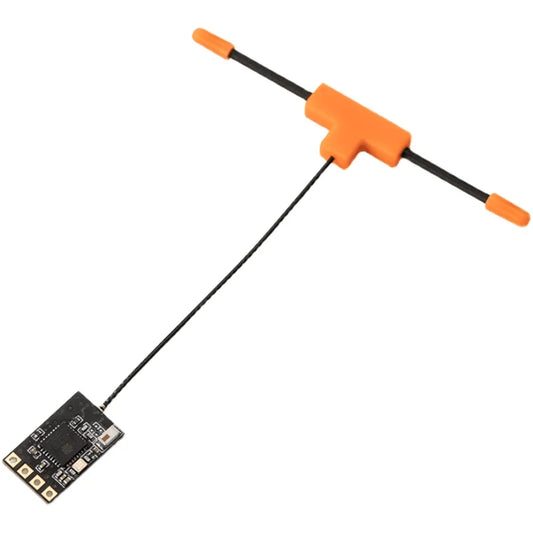
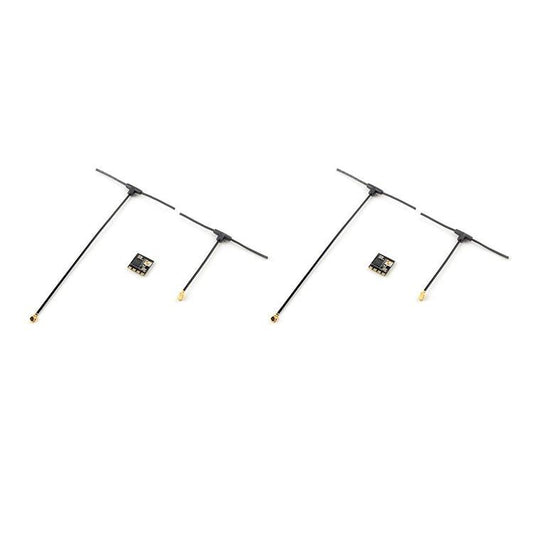
BAYCK ELRS 915MHz / 2.4GHz NANO ExpressLRS Receiver with T type Antenna Support Wifi upgrade for RC FPV Traversing Drones Parts
Regular price $24.33 USDRegular priceUnit price per$38.92 USDSale price $24.33 USDSale -
1.2GHz 10W 20W 25W / 1.4G 10W / 2.4G 10W Drone FPV Signal Amplifier Extender Signal Booster Drone Range Extender Tarot 1.2G FPV Image Transmissi
Regular price From $184.11 USDRegular priceUnit price per$220.93 USDSale price From $184.11 USDSale -
10W Anti Drone Module - 433M 800M 900M 1.2G 1.4G 1.5G 2.4GHZ UAV Countermeasure Module UAV Singal Amplifier RF Anti Drone
Regular price $79.17 USDRegular priceUnit price per$102.92 USDSale price $79.17 USDSale -
50W Anti Drone Module - 700-860mhz 850-940MHZ 940-1100mhz 2.4G 720-850MHZ 850-970MHZ 970-1100MHZ High Power Amplifier Module
Regular price $260.69 USDRegular priceUnit price per$312.83 USDSale price $260.69 USDSale -
50W Anti Drone Module - 900M 433M 868M 715M 1.2G 1.4G 1.5G 2.4G 5.8G 970-1030mhz 850-930 mhz Amplifier Module
Regular price From $273.99 USDRegular priceUnit price per$328.79 USDSale price From $273.99 USDSale -
30W Anti Drone Module - 900M 433M 800M 1.2G 1.4G 1.5G 2.4G 5.2G 5.8G Amplifier Module
Regular price $161.16 USDRegular priceUnit price per$193.39 USDSale price $161.16 USDSale -
100W Anti Drone Module - 433MHZ 800M 900M 1.2GHZ 1.4G 1.5G 2.4G High Power Amplifier Drone Countermeasure Modules UAV Jammers Type N Connector
Regular price $369.70 USDRegular priceUnit price per$443.65 USDSale price $369.70 USDSale -
45W Anti Drone Module - 900M 1.5G 2.4G 433M 45W1.4G Countermeasure Booster WIFI UAV Singal Amplifier With Gallium NEW Nitride Chip
Regular price $241.33 USDRegular priceUnit price per$289.59 USDSale price $241.33 USDSale -
60W Anti Drone Module - 433M 900M 1.5G 2.4G 1.2G 800M 1.4G UAV Countermeasure Module of Power Drone Signal Amplifier RF Amplifier Type N Connector
Regular price $287.02 USDRegular priceUnit price per$344.42 USDSale price $287.02 USDSale -
Drone Extender Dual Band 2.4GHz 5.8GHz Signal Booster for DJI Phantom Inspire Mini 3 Pro Mavic 3 Air 2 Spark Cendence Autel
Regular price $121.58 USDRegular priceUnit price per$145.89 USDSale price $121.58 USDSale -
2.4GHz 25W Drone DJI Mavic 3 FPV Signal Amplifier Extender Signal Booster Drone Range Extender Tarot 2.4G FPV Image Transmissi
Regular price From $184.11 USDRegular priceUnit price per$220.93 USDSale price From $184.11 USDSale -
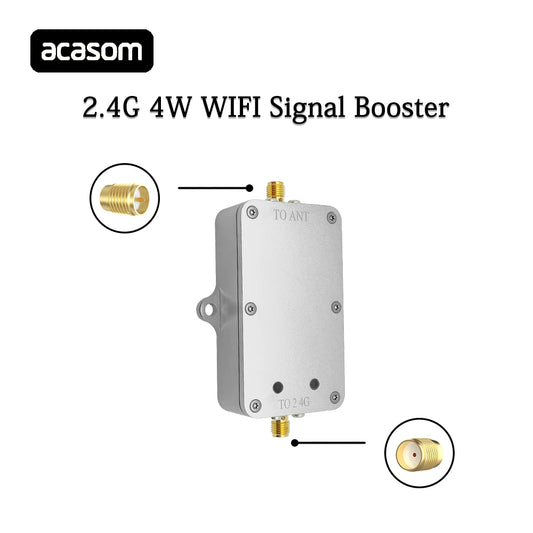
2.4GHz Wifi Drone 4W Range Extenders Signal Booster Wireless Broadband Amplifier Router 2.4Ghz Power Range Signal Booster
Regular price From $36.52 USDRegular priceUnit price per$47.48 USDSale price From $36.52 USDSale -
2.4G/5.8G 10W 8000mAh Dual-band Signal Booster Antenna Range Extender Remote for DJI Mavic 3, 3T, Matrix and Autel quadcopters
Regular price From $868.42 USDRegular priceUnit price per$1,042.11 USDSale price From $868.42 USDSale -
Dual Band DJI Drone Mavic Phantom Avata FPV Range Extender Amplifier 2.4G&5.8G Signal Booster
Regular price $87.65 USDRegular priceUnit price per$113.95 USDSale price $87.65 USDSale -
2.4GHz 4W Wifi Wireless Broadband Amplifier Router 2.4Ghz Power Range Signal Booster ZigBee Module
Regular price From $30.43 USDRegular priceUnit price per$39.57 USDSale price From $30.43 USDSale -
2.4GHz 5.8GHz WiFi6 WiFi6E Indoor Ceiling Antenna 2000-6000MHz Wideband Frequency
Regular price From $15.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per$21.00 USDSale price From $15.00 USDSale -
50W Anti-Drone Amplifier Module - 900M 433M 800M 1.2G 1.4G 1.5G 2.4G Frequencies Customized
Regular price $254.17 USDRegular priceUnit price per$305.00 USDSale price $254.17 USDSale -

2.4G 5.8G Dual Band Signal Amplifier - Signal Booster Extender For DJI Mavic Phantom Avata FPV Drone
Regular price $87.65 USDRegular priceUnit price per$113.95 USDSale price $87.65 USDSale -
2.4GHz 40W 46dBm RF High Power Amplifiers - wireless Signal Extender Sweep Signal Source For Drone WiFi6
Regular price From $91.30 USDRegular priceUnit price per$118.70 USDSale price From $91.30 USDSale -
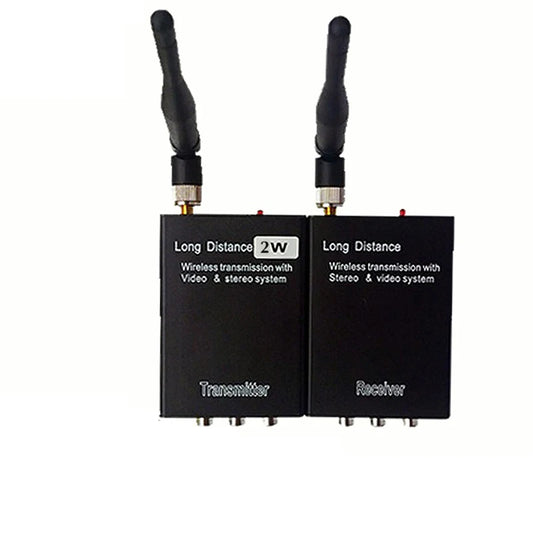
2.4G 2W 4CH VTX / VRX - 2000mw Wireless AV Video Sender + Receiver for cctv camera For Monitor
Regular price $84.79 USDRegular priceUnit price per$110.23 USDSale price $84.79 USDSale -
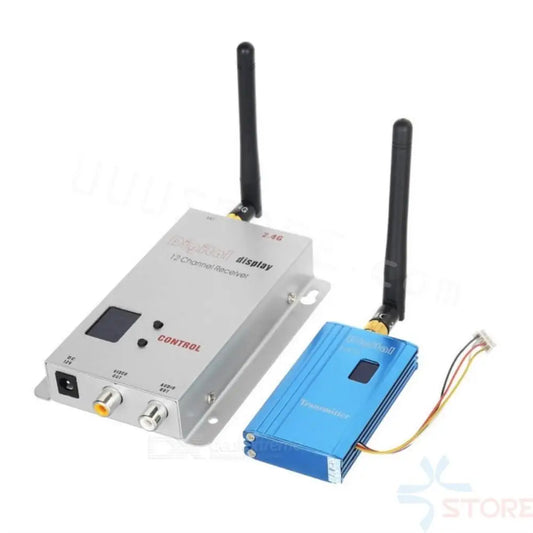
2.4G 1W 12CH VTX /VRX - Partom 2.4G 1000MW CCTV Wireless Video Transmitter and Receiver Kit UAV Drone Transceiver
Regular price From $63.60 USDRegular priceUnit price per$82.68 USDSale price From $63.60 USDSale -
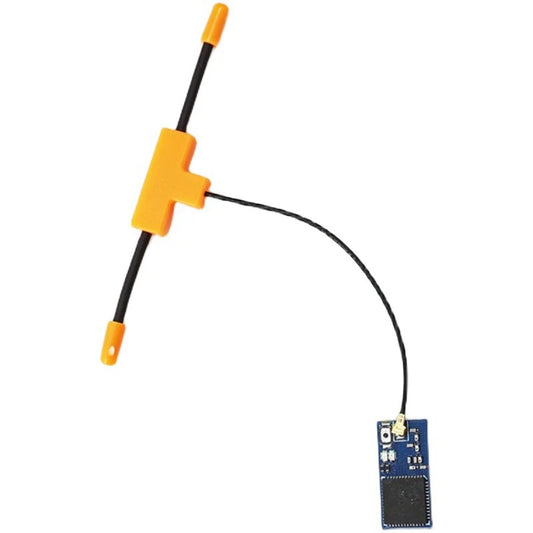
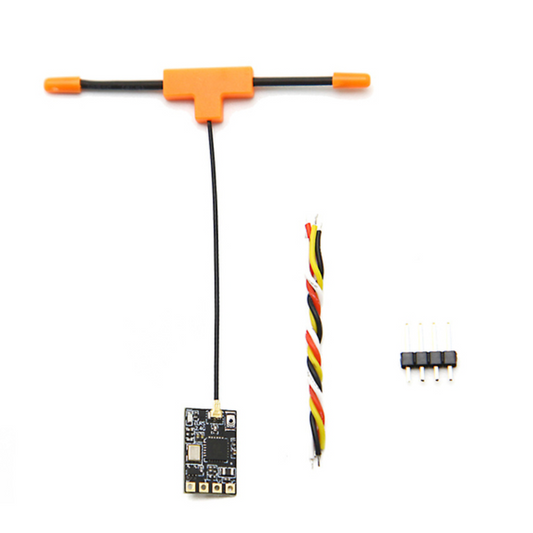
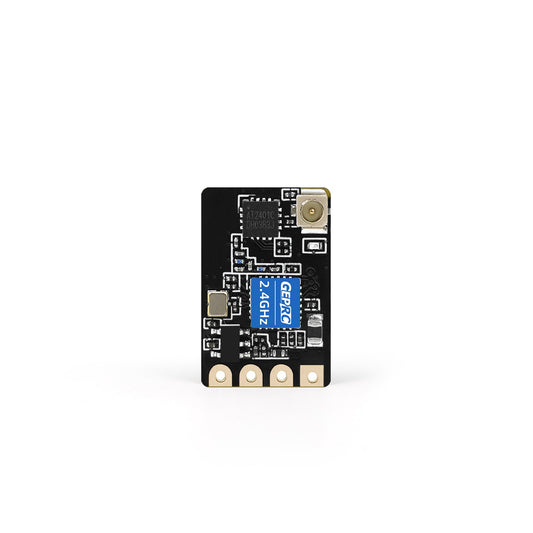
GEPRC ELRS Nano 2.4G PA100 Receiver
Regular price $27.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
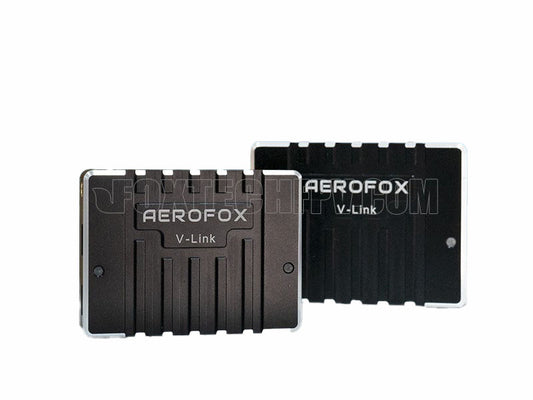
AEROFOX V-Link 15KM 30KM 800MHZ 1.4GHZ 2.4GHZ Long Range Video/Data Transmission System
Regular price From $1,699.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
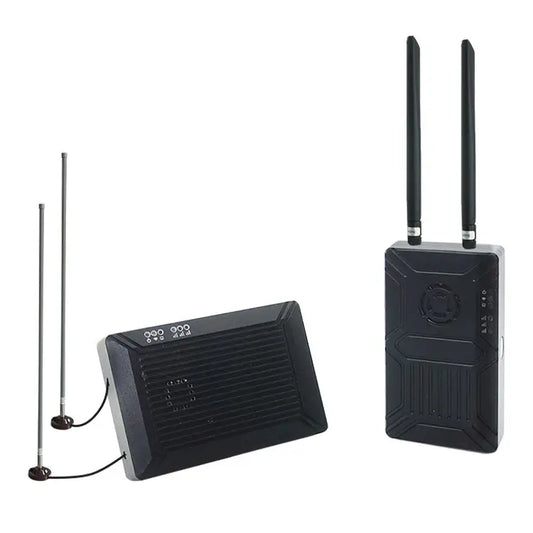
Foxtech VDC-7/VDC-15 - 1080P 60FPS 7KM 15KM 800MHz 1.4GHz 2.4GHz Long Range Video/Data/RC Transmission System
Regular price From $2,799.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
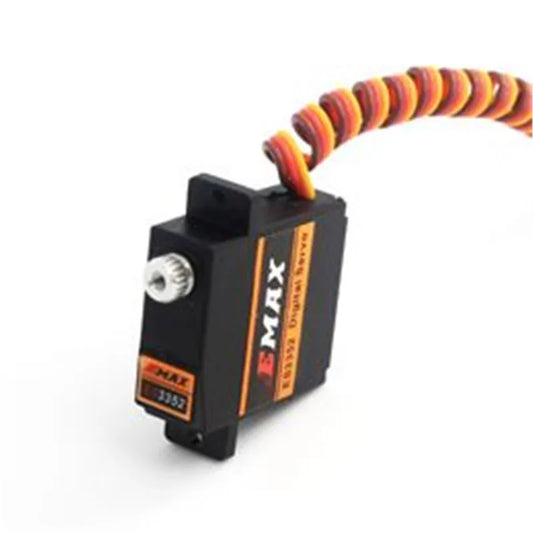
Emax ES3352 - 12.4g Mini Metal Gear Digital Servo For RC Airplane Gilder
Regular price $20.56 USDRegular priceUnit price per$28.79 USDSale price $20.56 USDSale -
Futaba R7014SB 2.4GHz 14CH FASSTest/FASST Receiver
Regular price $299.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
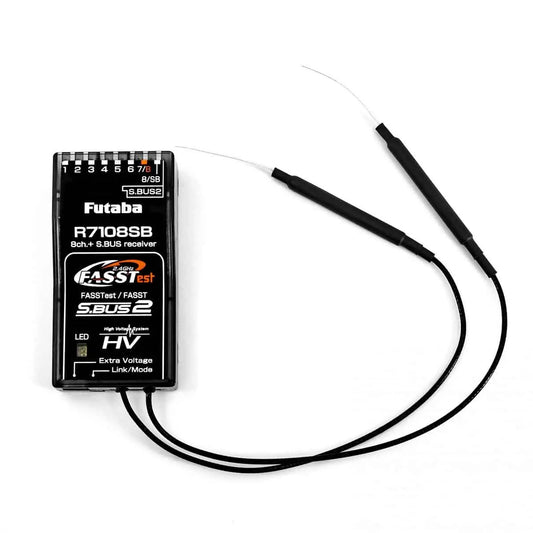
Futaba R7108SB 2.4GHz FASSTest/S.Bus2 8 Channel Receiver
Regular price $249.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
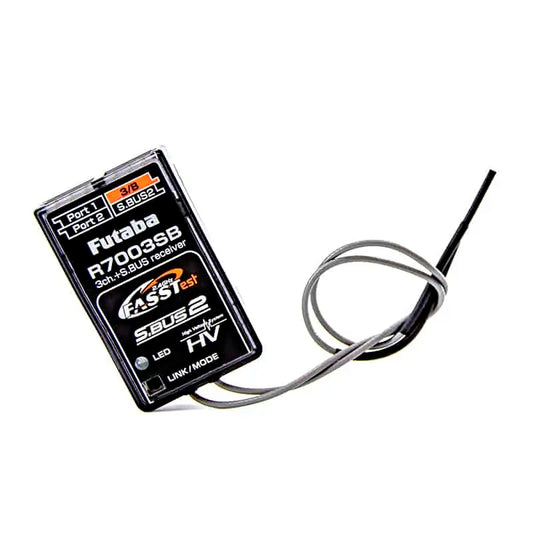
Futaba R7003SB Receiver - 2.4GHZ 3 Channels FASSTest Bi-Directional Communication System S.Bus/S.Bus2 Port Receiver
Regular price $145.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
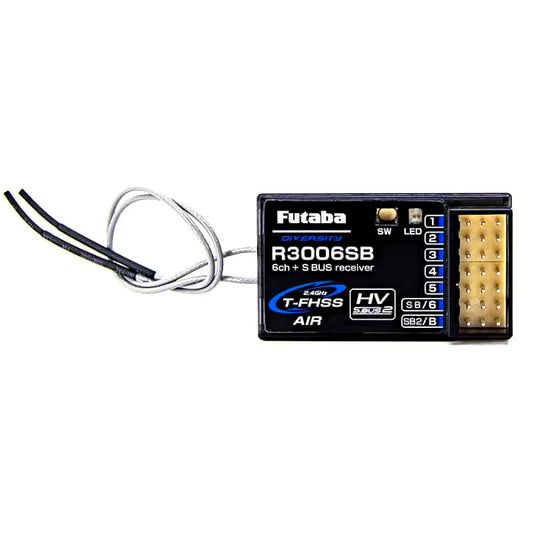
Futaba R3006SB Receiver - T-FHSS 2.4GHz 6 Channel SBus Full-range flight receiver
Regular price $90.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Futaba R3206SBM 6-Channel 2.4GHz T-FHSS S.Bus Port Micro Indoor Receiver
Regular price $60.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
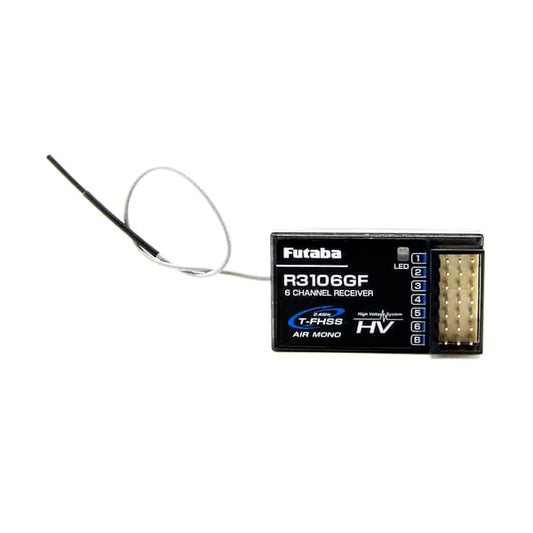
Futaba R3106GF 2.4GHZ 6-Channel T-FHSS Mono Receiver
Regular price $60.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
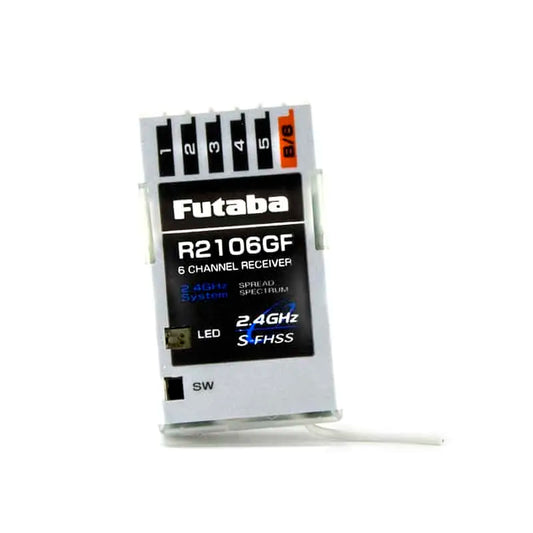
Futaba R2106GF 2.4GHz S-FHSS / FHSS 6-Channel Micro Receiver
Regular price $60.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Futaba R2000SBM - S-FHSS 2.4GHz S.Bus Port & RSSI Drone Racing Receiver
Regular price $49.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
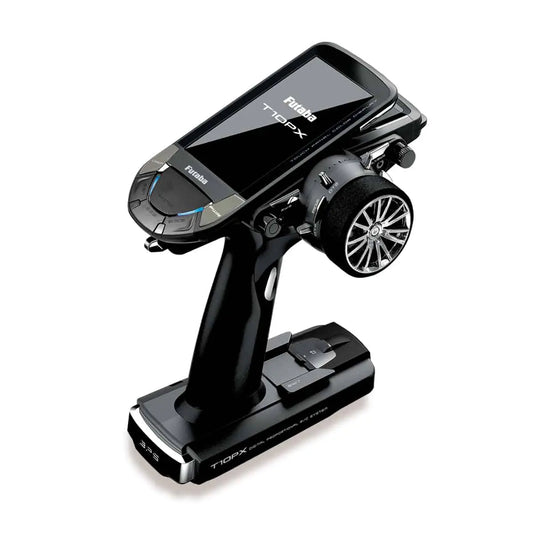
Futaba 10PX Transmitter - 10-Channel 2.4GHz T-FHSS SurfaceRadio System w/R404SBS Receiver
Regular price $959.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
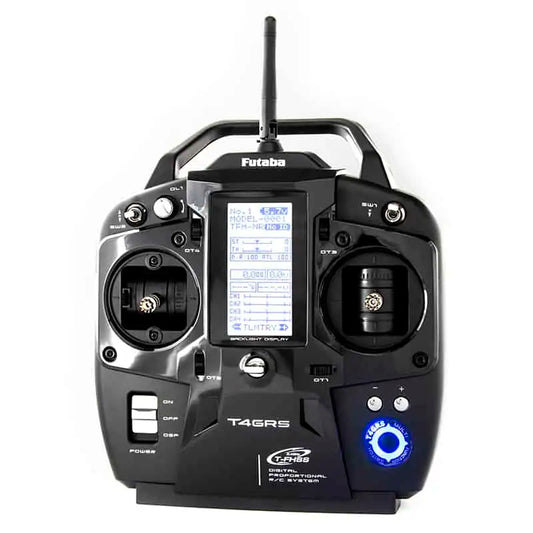
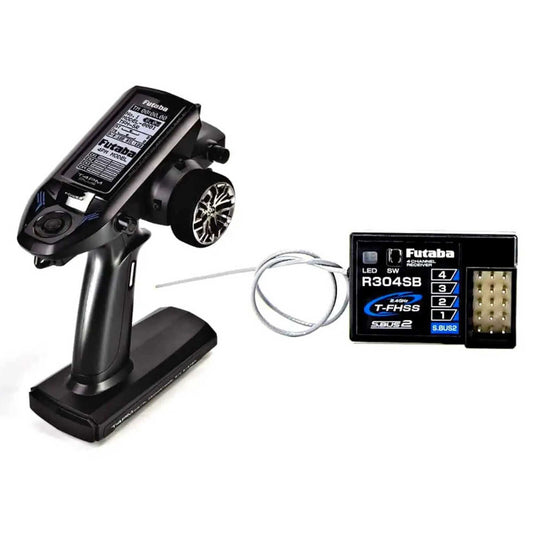
Futaba 4GRS 4-Channel 2.4GHZ Transmitter with R304SB Receiver for Surface Model
Regular price $469.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Futaba 4PM Plus Transmitter - 4-Channel 2.4GHz T-FHSS Radio System w/R334SBS Receiver for Surface Model
Regular price From $249.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Jumper R1 V2 Mini 2.4Ghz 16CH Receiver D16 Protocol SBUS Signal Tlite XT18S For RC Drone Durable Easy Install Easy To Use
Regular price $18.94 USDRegular priceUnit price per$26.51 USDSale price $18.94 USDSale -
Jumper ELRS Aion ELRS RX mini/mini SE/RX NANO 2.4GHZ 16CH Receiver - Compatible with 2.4 mode 5KM Range Transmitter for RC Drone
Regular price From $9.55 USDRegular priceUnit price per$14.32 USDSale price From $9.55 USDSale



































![0 EassTest 57533] 9 FASSTest Av](http://rcdrone.top/cdn/shop/files/R7014SB_2.webp?v=1707642252&width=533)