Agriculture Drone Accessories
Definition of Agriculture Drone Accessories: Agriculture drone accessories refer to the various components and parts that are used to enhance the functionality and performance of drones specifically designed for agricultural applications. These accessories are essential for carrying out tasks such as crop monitoring, precision spraying, mapping, and data collection in the agricultural sector.
Components of Agricultural Drones:
- Frame: The structure that holds all the components of the drone together.
- Motors: Provide the necessary power and thrust for the drone's flight.
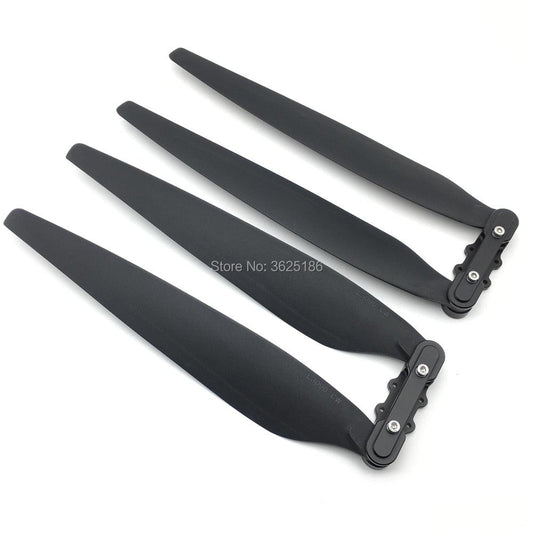
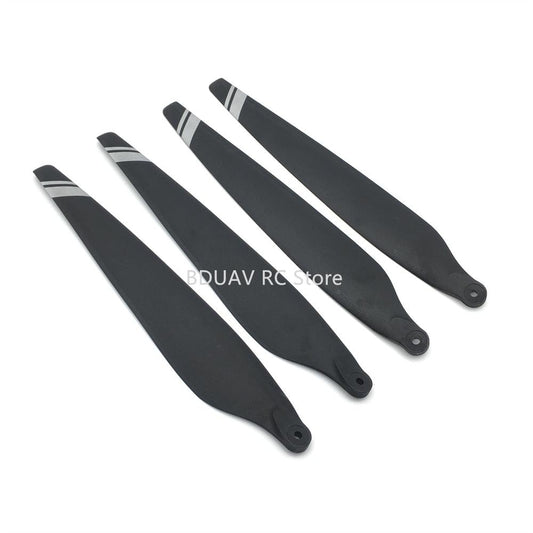
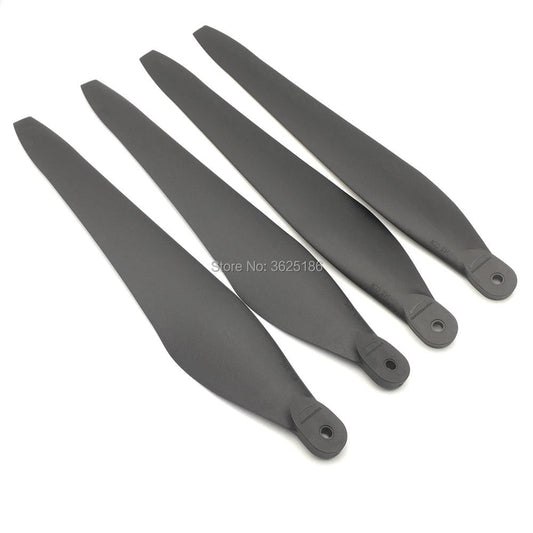
- Propellers: Generate lift and propulsion to keep the drone airborne.
- Flight Controller: The onboard computer that controls the drone's flight and navigation.
- Payload: The equipment or sensors attached to the drone for agricultural tasks, such as multispectral or thermal cameras, LiDAR, or spraying systems.
- Battery: Provides the electrical power to the drone's motors and electronics.
- Transmitter and Receiver: Enable remote control of the drone's flight and communication between the operator and the drone.
- GPS Module: Provides accurate positioning and navigation data to the drone.
- Telemetry System: Allows real-time monitoring of the drone's flight parameters and sensor data.
- Data Storage and Transmission: Devices or systems for storing and transmitting the collected data.
- Landing Gear: Supports the drone during takeoff and landing.
Parameters and Selection Methods of Agricultural Drone Accessories:
- Payload Compatibility: Ensure that the accessories, such as cameras or spraying systems, are compatible with the drone's payload capacity and mounting options.
- Flight Time: Consider the battery capacity and efficiency of the motors to determine the flight time and endurance of the drone.
- Range and Signal Strength: Check the range and signal strength of the transmitter and receiver system to ensure reliable communication between the operator and the drone.
- Sensor Quality and Accuracy: Evaluate the specifications and performance of sensors, such as cameras or LiDAR, to meet the specific requirements of agricultural tasks.
- Construction and Durability: Choose accessories made from high-quality materials that can withstand the demands of agricultural environments.
DIY Agricultural Drones: To DIY an agricultural drone, you can follow these general steps:
- Research and Plan: Understand the specific requirements and tasks you want your agricultural drone to perform.
- Select Components: Choose the appropriate frame, motors, propellers, flight controller, payload, and other necessary components based on your requirements.
- Assembly: Follow the instructions provided with each component and assemble the drone carefully.
- Wiring and Configuration: Connect the components properly, set up the flight controller, and configure the parameters and settings.
- Testing and Calibration: Conduct thorough testing and calibration of the drone to ensure proper functionality and stability.
Maintenance of Agricultural Drones:
- Regular Inspection: Inspect the drone for any signs of wear, damage, or loose connections before and after each flight.
- Cleaning: Keep the drone and its components clean from dirt, dust, and debris. Use compressed air or a soft brush to remove any particles.
- Battery Care: Follow the manufacturer's guidelines for proper battery maintenance, including storage, charging, and handling.
- Propeller Maintenance: Check the propellers for any signs of damage or imbalance. Replace damaged or worn-out propellers.
- Firmware and Software Updates: Keep the drone's firmware and software up to date to ensure optimal performance and access to new features.
Operation of Agricultural Drones:
- Pre-flight Checklist: Conduct a pre-flight checklist to ensure that all components are functioning correctly, and the drone is in good condition.
- Flight Planning: Plan the flight path and survey area, considering safety, regulations, and specific agricultural tasks.
- Flight Execution: Follow the proper procedures for takeoff, navigation, data collection, or spraying operations, while maintaining situational awareness.
- Data Processing: Process and analyze the collected data using suitable software or tools to derive meaningful insights for agricultural applications.
FAQ: Q: Can I use any drone for agricultural purposes? A: While general-purpose drones can be adapted for some agricultural tasks, specialized agricultural drones offer specific features and capabilities tailored for agricultural applications.
Q: What payload is suitable for agricultural mapping and monitoring? A: Multispectral cameras, thermal cameras, or LiDAR sensors are commonly used for agricultural mapping and monitoring tasks.
Q: How can I maintain accurate and consistent spraying with an agricultural drone? A: Proper calibration of the spraying system, including nozzle selection, flow rate adjustment, and accurate flight planning, is crucial for accurate and consistent spraying.
Q: Can I fly an agricultural drone in adverse weather conditions? A: It is generally not recommended to fly agricultural drones in adverse weather conditions such as strong winds, rain, or fog, as it may affect flight stability and compromise safety.
Q: Are there any legal regulations or permits required for using agricultural drones? A: The use of agricultural drones is subject to local regulations and permits. It is important to familiarize yourself with the applicable rules and obtain any necessary permissions before operating an agricultural drone.
Please note that specific guidelines and considerations may vary depending on the country or region of operation. It is recommended to consult local authorities and adhere to legal requirements and safety guidelines when using agricultural drones.