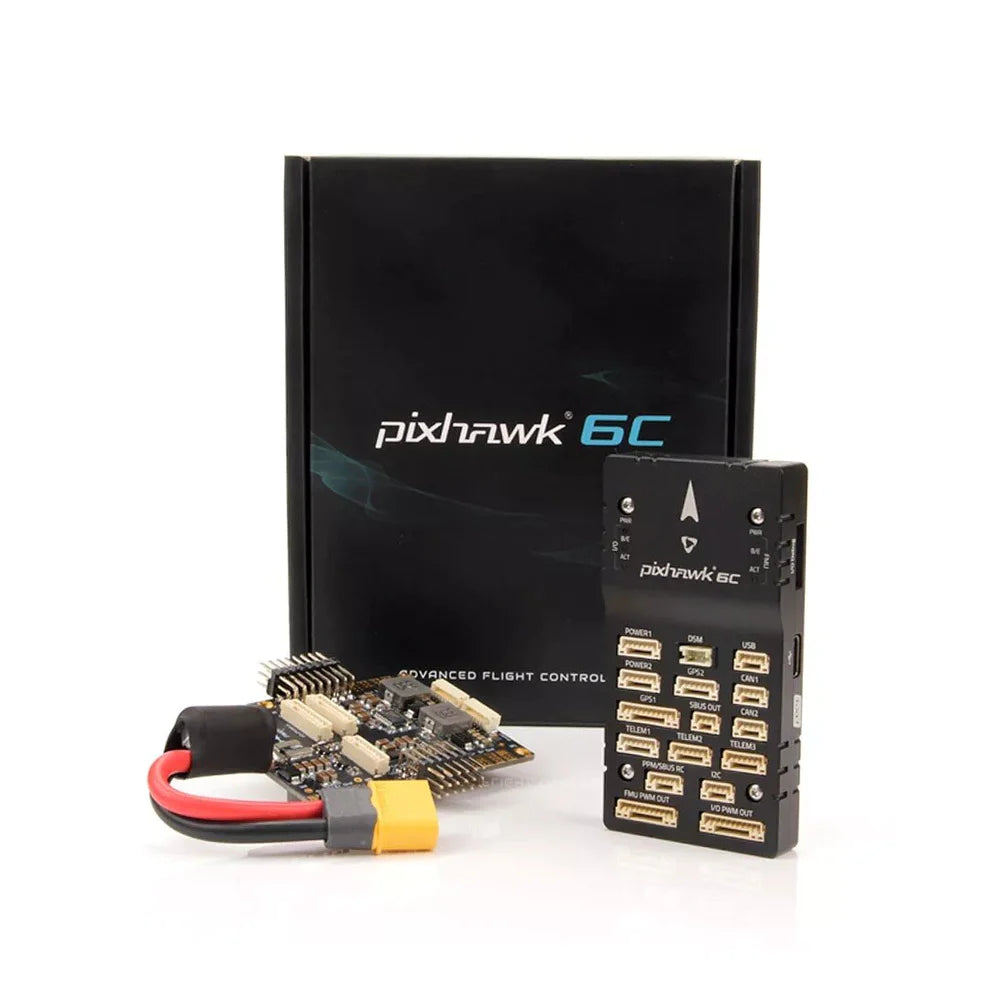
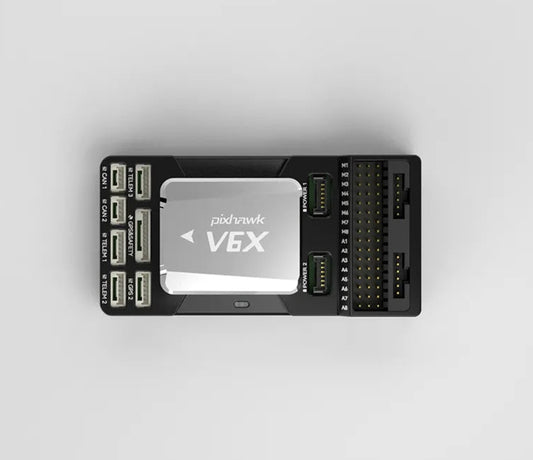
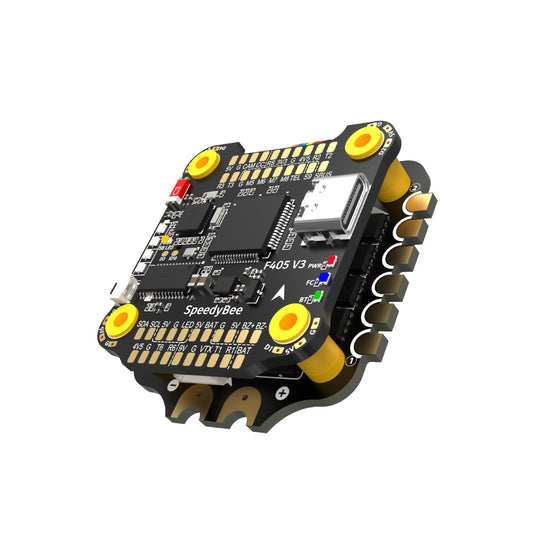
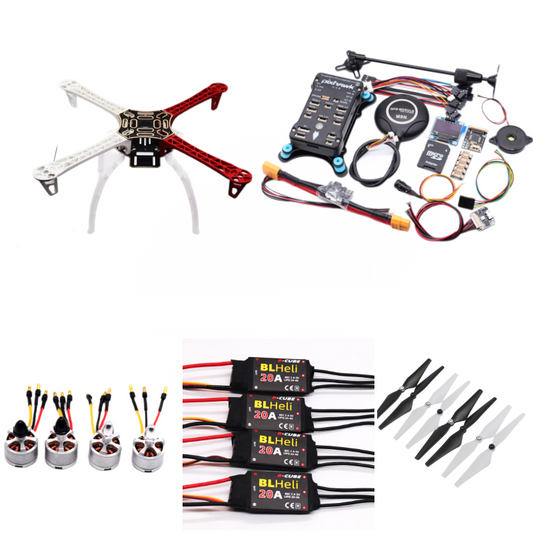
Flight Controller Type
-

Flight Controller Stacks
Explore our premium selection of flight controller stacks for FPV drones, featuring...
-

F4 Flight Controller
F4 Flight Controller Collection features versatile and high-performance boards designed for FPV...
-

F7 Flight Controller
F7 Flight Controller Collection delivers enhanced computing power and features over F4-based...
-

H7 Flight Controller
The H7 Flight Controller Collection features a range of advanced autopilot systems...
-

Betaflight Flight Controllers
The Betaflight Flight Controller is a popular, high-performance controller designed specifically for...
-

INAV Flight Controllers
Explore the INAV Flight Controllers collection—precision-tuned for fixed-wing, multirotor, and VTOL drones....
-

Ardupilot Flight Controller
Explore our ArduPilot Flight Controller Collection, featuring powerful, open-source flight controllers from...
-

PX4 Flight Controllers
The PX4 Flight Controller collection offers open-source, high-performance autopilot systems for drones,...
-

SpeedyBee Flight Controllers
SpeedyBee offers a versatile range of high-performance flight controllers for FPV drones,...
-

Matek Flight Controller
The Matek Flight Controller collection offers a wide range of high-performance flight...
-

Kakute Flight Controller
The Kakute Flight Controller series by Holybro is designed for FPV drones,...
By Flight Controller Application
-

FPV Flight Controller
The FPV Flight Controller collection offers a wide range of powerful FCs—from...
-

Fixed Wing Flight Controller
Explore our premium range of Fixed Wing Flight Controllers, engineered for fixed-wing...
-

Agriculture Drone Flight Controller
The flight controller (FC) acts as the brain of an agricultural drone,...
-

Industrial Flight Controller
Unlock precision and performance with our Industrial Flight Controller collection, featuring top-tier...
-

VTOL Flight Controller
The VTOL Flight Controller features advanced flight controllers designed for Vertical Takeoff...
Flight Controller Brand
-

JIYI Flight Controller
JIYI specializes in advanced autopilot systems for agricultural and industrial drones. Its...
-

Holybro Autopilot Flight Controller
Explore the Holybro Autopilot Flight Controller series, featuring advanced solutions for fixed-wing,...
-

CUAV Autopilot Flight Controller
CUAV Autopilot Flight Controllers offer industrial-grade performance and compatibility with PX4...
-

iFlight Flight Controller
iFlight Flight Controllers: Precision Control for FPV Drones iFlight offers high-performance flight...
-

GEPRC Flight Controller
Discover the GEPRC Flight Controller collection—high-performance AIO and stack systems for FPV...
-

BOYING Flight Controller
Explore the BOYING Flight Controller collection, designed for precision agriculture drones. Featuring...
-
SpeedyBee F405 V4 BLS 55A 30x30 FC&ESC Stack
Regular price From $49.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
SpeedyBee F405 V4 BLS 60A 30x30 FC&ESC Stack
Regular price $99.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Holybro Pixhawk 6X (ICM-45686) Flight Controller – Triple Redundant IMU, STM32H753, Ethernet, PX4 & ArduPilot Compatible
Regular price From $111.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
CUAV Pixhawk V6X Autopilot PX4 Ardupilot Flight Controller - STM32H753IIK6 Processor RM3100 Compass Customize Carrier Board and Core With NEO 3 Pro
Regular price From $380.95 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
SpeedyBee F405 V3 - 3-6S 30X30 FC&ESC FPV Stack BMI270 F405 Flight Controller BLHELIS 50A 4in1 ESC for FPV Freestyle Drone Model
Regular price $95.76 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
SpeedyBee F405 V5 OX32 55A 30x30 Model Aircraft FC & 4-in-1 ESC Stack with ICM42688 Gyro, STM32F405, Wireless Tuning & 16MB Blackbox
Regular price From $69.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
SpeedyBee F405 AIO 40A Bluejay 25.5x25.5 3-6S Flight Controller
Regular price $79.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Foxeer F722 V4 Mini MPU6000 Flight Controller
Regular price $85.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
SpeedyBee F7 V3 Flight Controller
Regular price $63.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
SpeedyBee F405 Mini BLS 35A 20x20 Stack
Regular price From $42.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Matek H743-SLIM Flight Controller with OSD - 5V BEC MPU6000 Built-in OSD No Current Sensor for RC Racing Drone Multirotor Multicopter
Regular price $114.54 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Holybro Kakute H743-Wing Autopilot Flight Controller - Layout Specifically For Fixed Wing & VTOL Applications With M9N M10 GPS Module
Regular price From $125.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Holybro Pixhawk Jetson Baseboard Bundle With 6X / 6X Pro and NVIDIA Jetson
Regular price From $0.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Flywing ACE Helicopter Flight Control FBL Gyro H1 Upgraded Version with Built-in M10 GPS and Coordinated Turn
Regular price $239.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
PIXHAWK2.4.8 Flight Control F450 Drone Kit - Ardupilot 100MW Radio Telemetry Quadcopter BLHELI 20A 2212 Motor ESC Landing Gear
Regular price From $243.30 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
SpeedyBee F405 WING APP ArduPilot INAV 2-6S Flight Controller for RC Multirotor Airplane Fixed-Wing Drone
Regular price $55.73 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
SpeedyBee F7 V3 BL32 50A 30x30 Stack Blackbox Data Analyze iNAV Betaflight Emuflight Wireless Firmware Flasher
Regular price From $65.40 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Holybro Pixhawk 4 Autopilot Flight Controller
Regular price From $0.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Holybro Pixhawk 6X Pro Autopilot Flight Controller
Regular price From $709.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Matek Mateksys Flight Controller - 2022 NEW H743-WING V3 H743 Wing for FPV Racing RC Drone Fixed Wings
Regular price $156.18 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
(1MB FLASH) GOKU GN 745 40A AIO BL_32 V1.2 (MPU6000 ) 25.5 X 25.5 5V/9V
Regular price $143.19 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
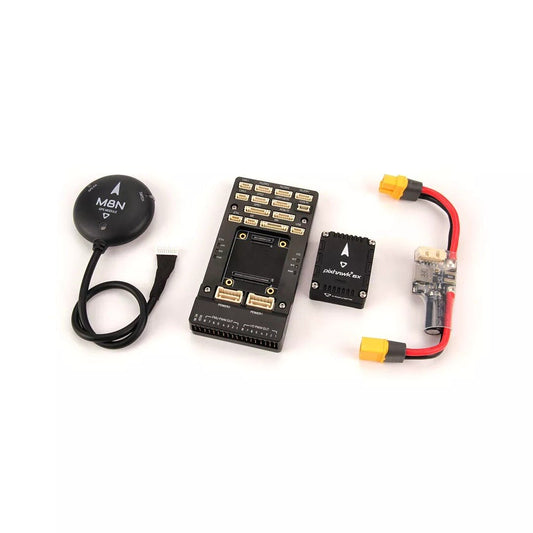
Pixhawk 2.4.8 PX4 PIX 32 Bit Flight Controller - M8N GPS / Wifi Telemetry Module / Safety Switch Buzzer RGB I2C 4G SD OSD / OLED
Regular price From $10.96 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Holybro Pixhawk 6C Mini Flight Control - FC With M02 M06 Power Module and M8N M9N M10 GPS For Rc autonomous vehicle/Quadcopter/Airplane/Drone
Regular price From $233.65 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
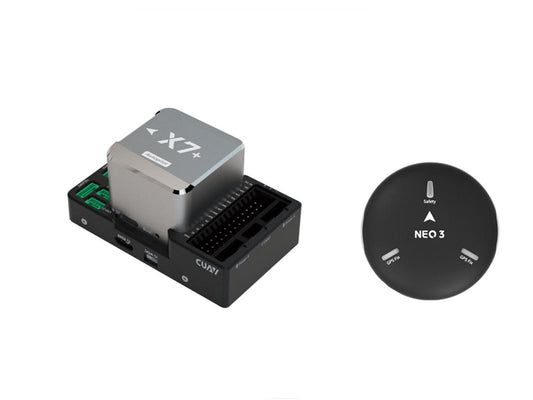
CUAV NEW X7+ Flight Controller NEO 3 Pro GPS Pixhawk Open Source PX4 ArduPilot GNSS FPV RC Drone VTOL Quadcopter Combo
Regular price From $407.11 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
MATEK Mateksys FLIGHT CONTROLLER F405-HDTE
Regular price $95.15 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
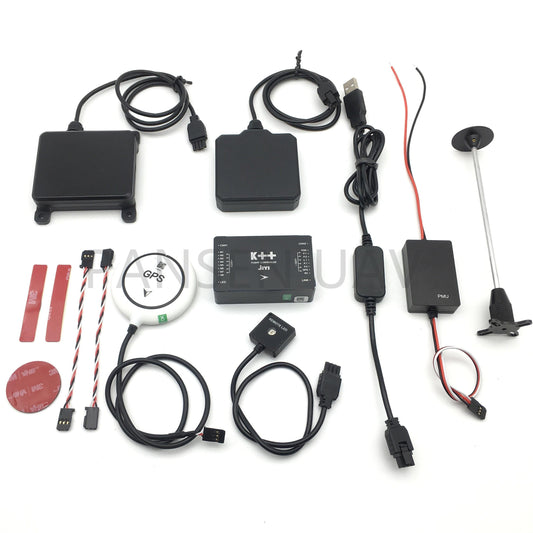
JIYI K++ Flight Control - Dual CPU optional obstacle avoidance radar Special Autopilot FC for Agricultural Drone
Regular price From $49.27 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
MATEK F405-VTOL Flight Controller - Baro OSD MicroSD Card Blackbox 2-6S LiPo ArduPilot INAV for RC Multirotor Fixed-Wing Airplane
Regular price From $83.29 USDRegular priceUnit price per -

GEPRC TAKER F722 BLS 80A V2 Stack – STM32F722 FC + 80A 4in1 ESC for 3–6S High-Performance FPV Drones
Regular price $155.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Holybro Kakute H7 V2 Flight Controller
Regular price $120.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
GEPRC GEP-F411-35A AIO - (F411 FC 35A 2-6S 8bits BLS ESC 26.5mm/M2) For DIY RC FPV Quadcopter Drone Replacement Accessories Parts
Regular price $115.60 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
ATOMRC Fixed Wing Flight Controller F405 NAVI Mini for Swordfish
Regular price $53.25 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
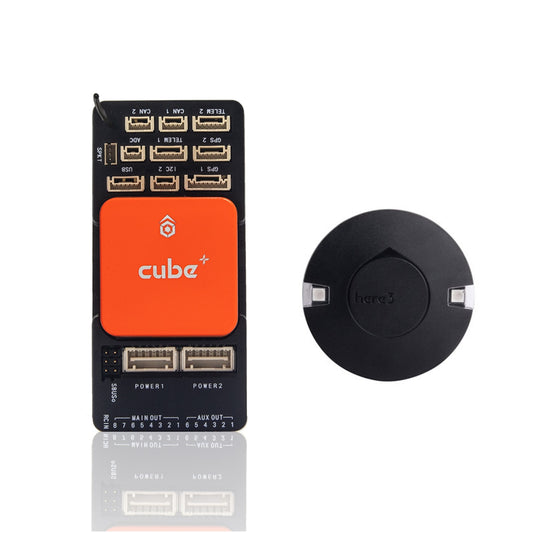
HEX Pixhawk 2.1 PX4 PIX 32 Bit Autopilot Flight Controller - The Cube Orange + Standard Set W/ Here 3 GPS & ADS-B Carrier Board
Regular price From $290.74 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Holybro Pixhawk 6X Autopilot Flight Controller - Module Standard Base Mini Base H753 PM02D M8N M9N M10 GPS for RC Multirotor Airplanes Drone
Regular price From $122.16 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
APM2.8 APM 2.8 flight controller Ardupilot +M8N GPS built-in compass +gps stand+shock absorber for RC Quadcopter Multicopter
Regular price From $104.90 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
MATEK H743-SLIM V3 - Mateksys FLIGHT CONTROLLER
Regular price $139.39 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Flywing H2 Helicopter Flight Control FBL Gyro (H1 Upgraded Version) with Dual GPS, CAN Bus, 12S Voltage Detection
Regular price $299.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per