-
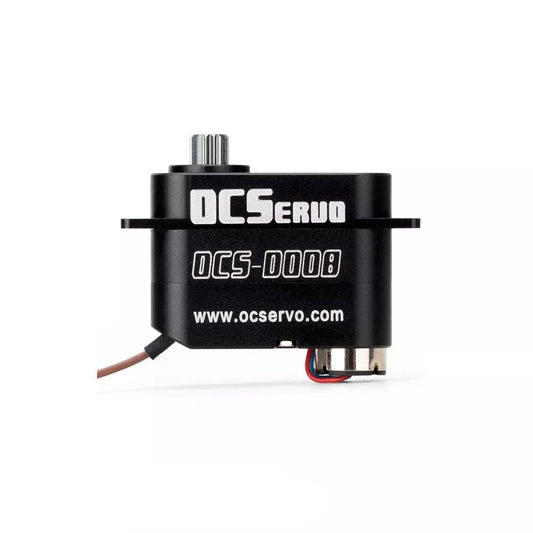
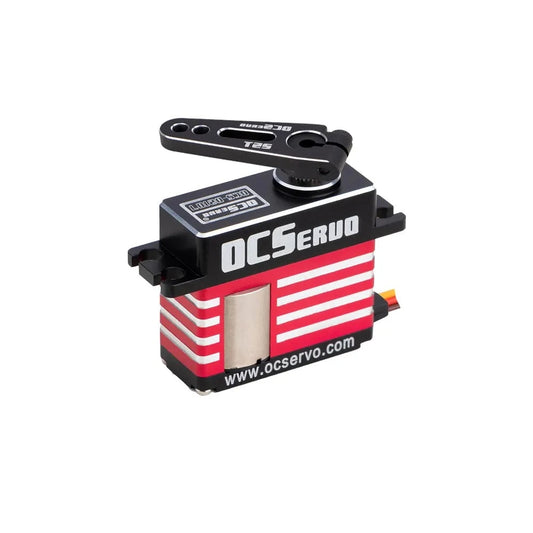
OCServo OCS-D008 - 7.4V 3.2kg.cm 7.7g 0.07S/60° Coreless Motor Micro Servo Metal Gear All CNC Case
Regular price $28.45 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
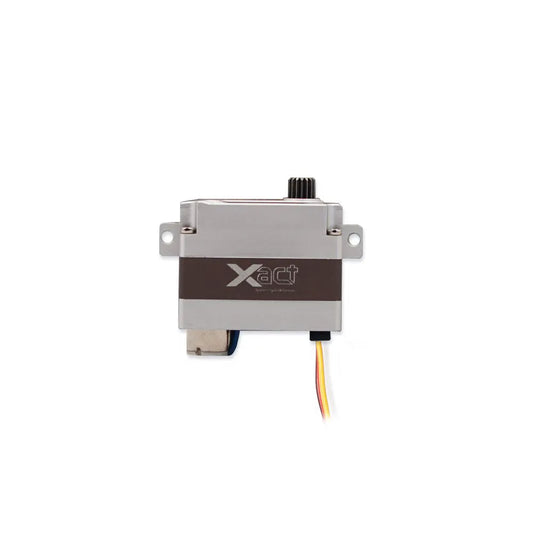
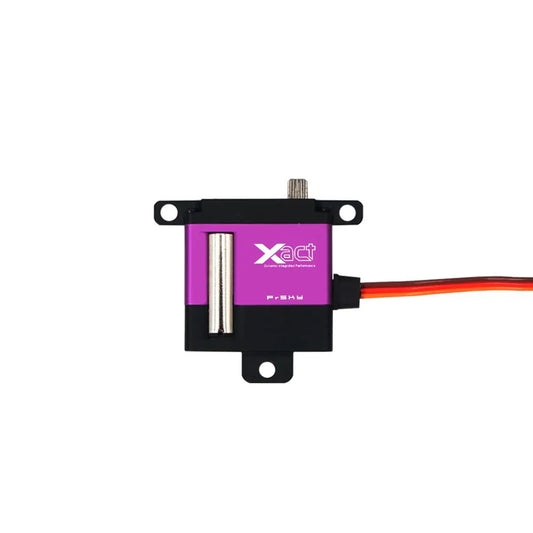
FrSky Coreless Xact 5600 Series Servos - WING 3.7V 4.2V 8.4V 2.10 kgf.cm - 4.8kgf.cm Capable Servos Xact HV5611/HV5612/W5651H/W5652H
Regular price $59.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FEETECH SCS2332 Servo Motor, 6V Serial BUS, Coreless, Metal Gear, 4.5kg.cm Torque, 300° Range, TTL Half-Duplex
Regular price From $45.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Futaba S9177SV 41kg High-Torque 0.11s S.Bus2 Coreless HV Airplane Servo (No BEC Use)
Regular price $179.99 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
4X Coreless servo 25kg 35KG high speed servo pro digital and Stainless Steel gear servo arduino servo for Robotic DIY,RC car
Regular price From $85.42 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
JX Servo CLS6336HV CLS6322HV 35kg 21KG Torque High Voltage High-precision Metal Coreless Digital Servo For RC Helicopter Car
Regular price From $37.08 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
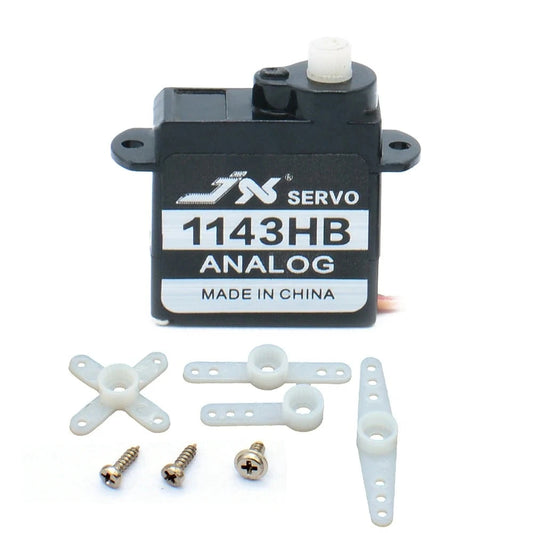
JX Servo PS-1143HB - 4.8-6.0V 0.55kg 0.08sec/60 3.7g Plastic Gear Mini Coreless Analog Servo JR Plug For Fixed-wing Helicopter RC Model
Regular price From $9.48 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
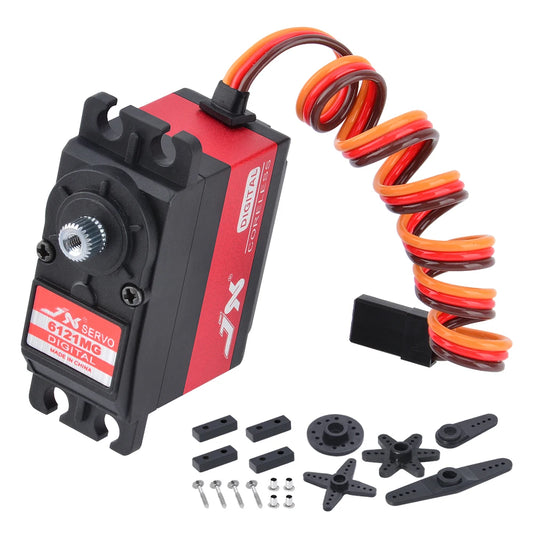
JX Servo PDI-6121MG - 6V 21KG 0.13sec 120° High Precision Metal Gear Digital Coreless Standard Servo For RC Model
Regular price From $30.06 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
OCServo OCS-D2107 - 8.4V21kg.cm 0.07S/60° Digital Mid Servo High Vottage High Torque Coreless servo
Regular price From $44.91 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
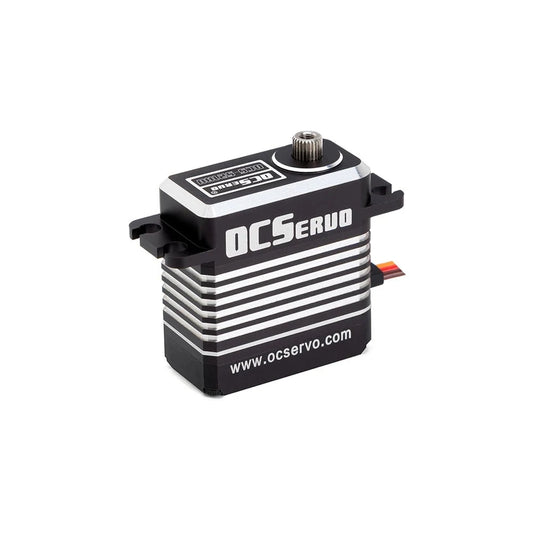
OCServo OCS-521HV - 8.4V 52kg.cm 81g 0.12S/60° Coreless Motor High Voltage High Torque Servo Steel Gear All CNC Case Waterproof
Regular price From $68.66 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FrSky Coreless Xact 5100 Series Servos WING HV 8.4V Capable HV5101
Regular price $59.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FrSky Coreless Xact 5700 Series Glider Servos H5701 for F5K/D5701 for F3K DLG 3.7v - 8.4v 1.40kgf.cm - 2.30kgf.cm
Regular price $50.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
MKS HV1250 7.4V Titanium Gear Coreless HV Digital Servos Motor for 1/10 RC Buggy/Heli
Regular price $168.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
MKS DS9910 High Torque Coreless Servo Motor 4.8V–7.0V
Regular price $209.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
OCSERVO OCS-D1102 11 kg.cm High Voltage Digital Micro Wing Servo, Coreless Motor, CNC Aluminum Case
Regular price From $59.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per$0.00 USDSale price From $59.00 USD -
FEETECH FT2331M Servo Motor, 4.8–6V Coreless, Metal Gear, 0.07s/60°@6V, 3.5kg.cm, 25T Spline, Aluminium Case
Regular price From $30.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FEETECH STS3032-C036 Servo Motor, 6V 360° Double Shaft Serial Bus, Magnetic Encoder, 4.5kg.cm Torque, Coreless
Regular price From $40.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FEETECH SM85CL Servo Motor, 12V RS485 Bus, 85kg.cm Stall Torque, Coreless, Aluminium Case, 360°, Feedback
Regular price From $212.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FEETECH SM60CL Servo Motor, 12V RS485 Serial, 60kg.cm Stall, Steel Gears, 360° Range, Coreless, 35RPM No-Load
Regular price From $168.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FEETECH STS3045 Servo Motor, Coreless Metal Gear, 6V 6kg 360°, 4.8–7.4V, Serial Bus, Feedback, 25T Spline
Regular price From $52.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FEETECH HL-3915 Servo Motor, 12V TTL Serial Bus, Coreless Metal Gear, 0–360° Control, 14.2kg.cm Torque, PID
Regular price From $65.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FEETECH HL-3606 Servo Motor, TTL Double Shaft, 6V 6kg.cm, Coreless, 0–360° PID, Half‑Duplex (ST-3006-C001/C002)
Regular price From $65.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FEETECH HL-3935 Servo Motor, 12V 35kg.cm Double Shaft Serial Bus, Coreless, 0–360° PID Control, 1 Mbps, Aluminium
Regular price From $117.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FEETECH HL-3955 Servo Motor, 12V Coreless, 55kg.cm Stall Torque, Double Shaft, PID Control, 360°/Multi‑turn UART
Regular price From $117.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FEETECH FT1190M Servo Motor, Coreless Digital, 200° Travel, Metal Gear, 3.5kg.cm @6V, 20T/3.95mm Spline
Regular price $26.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FEETECH FI7622M Servo Motor, 7.4V 25kg.cm Digital 180° Coreless, Metal Gear, Ball Bearings, PA+Alumi num Case
Regular price $45.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FEETECH FT5420M Servo Motor, 180° Steel Gear Coreless Digital, 22.5kg.cm Peak Stall @ 8.4V, 0.095sec/60°
Regular price $33.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FEETECH FT2304M Servo Motor, 6V 3.0kg.cm Digital Coreless, 120° Travel, Metal Gears, 3.5V-8.4V, 0.08sec/60°@6V
Regular price $55.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FEETECH FT9015M Servo Motor, 7.4V 15kg.cm Digital Coreless, Metal Gear, 180° PWM Travel, 25T Spline, Aluminum Case
Regular price $65.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FEETECH FT9025M Servo Motor, 4.8–6V Coreless, Metal Gear, 8.5kg.cm @6V, 0.133sec/60°, 180° PWM Control
Regular price $52.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FEETECH SCS46 Servo Motor, SC-4600-C001, 7.4V, 40.5kg.cm, 300° Bus Serial, Coreless, Steel Gears, Aluminium Case
Regular price From $110.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FEETECH STS3250 Servo Motor, 12V 50kg.cm, Magnetic Encoder Double Shaft TTL, Coreless, 25T Spline, Steel Gear, 360°
Regular price From $115.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Savox SV-1250MG+ Digital HV Coreless Metal Gear Micro Servo, 7.4V, 8kg Torque, 0.10s Speed
Regular price $96.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Futaba RS303MR 7.4V TTL/PWM Robot Servo, 6.5kg Torque, 0.11s Speed, 300° Coreless Metal Gear
Regular price $59.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Futaba S9370SV High-Voltage Servo | Coreless Motor, S.Bus2, Titanium Gears for RC Car & Boat
Regular price $139.99 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
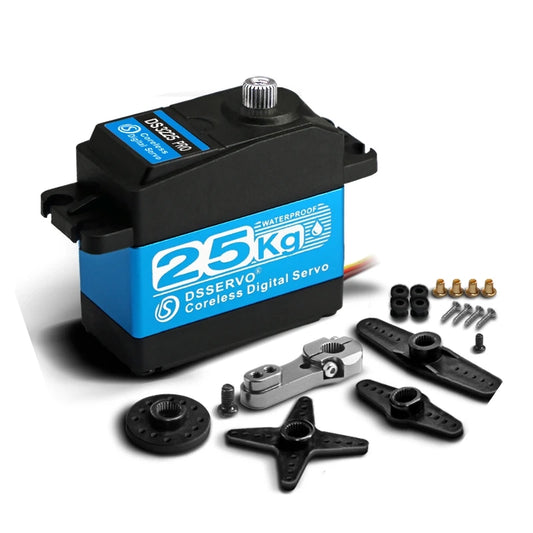
DSServo DS3225 DS3235 Pro - Coreless servo 25kg 35KG high speed servo pro digital and Stainless Steel gear servo arduino servo for Robotic DIY,RC car
Regular price From $25.70 USDRegular priceUnit price per