By Radio Type
-

Drone Transmitter
The Drone Transmitter collection features an extensive range of remote controllers, TX...
-
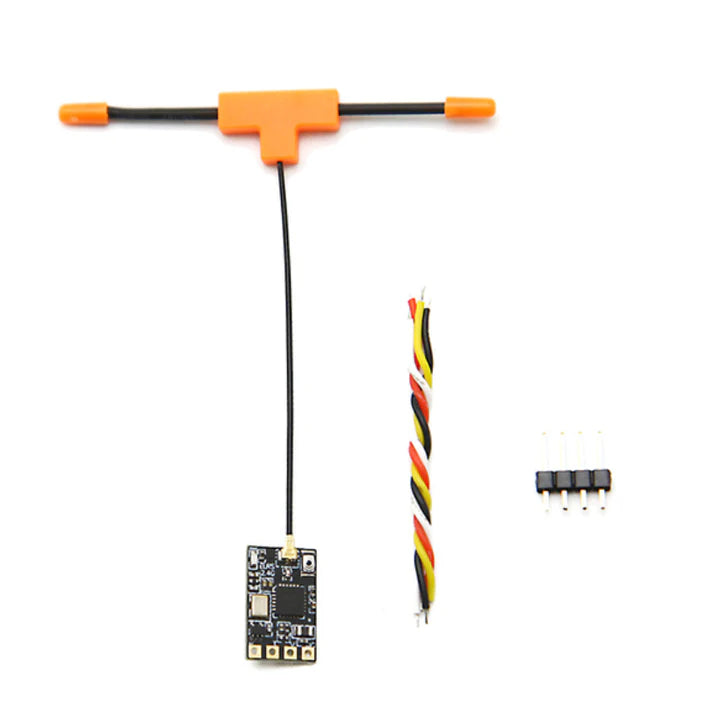

Drone Receiver
The Drone Receiver collection features a wide range of FPV receivers from...
-

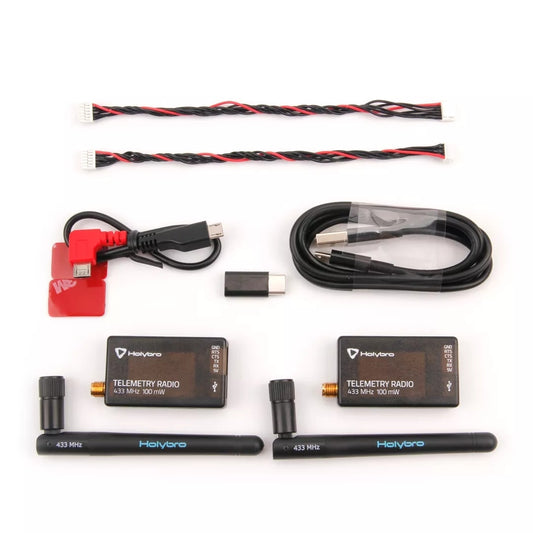
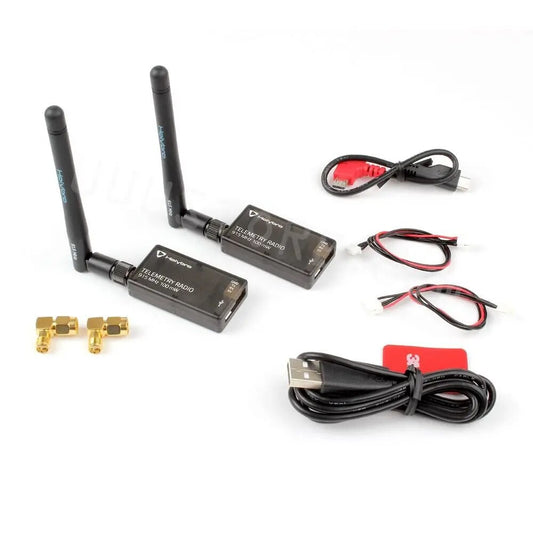
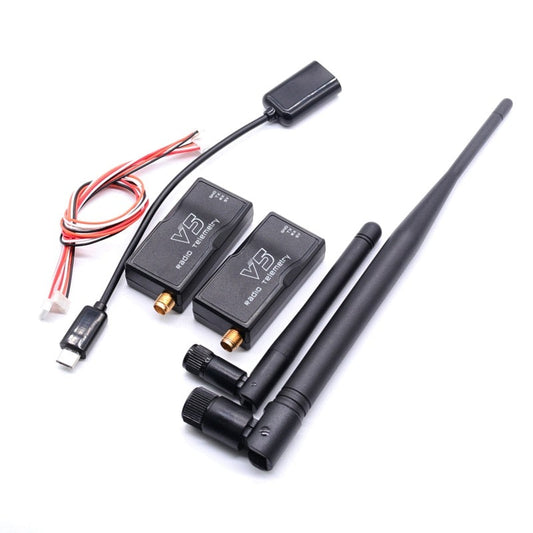
Radio Telemetry
Radio telemetry systems provide long-range, real-time data transmission between UAVs and...
-

Surface Transmitter
Discover our premium selection of RC surface transmitters designed for RC cars,...
-

Drone Ground Station
Explore our advanced drone ground control stations designed for agriculture, industrial inspections,...
-
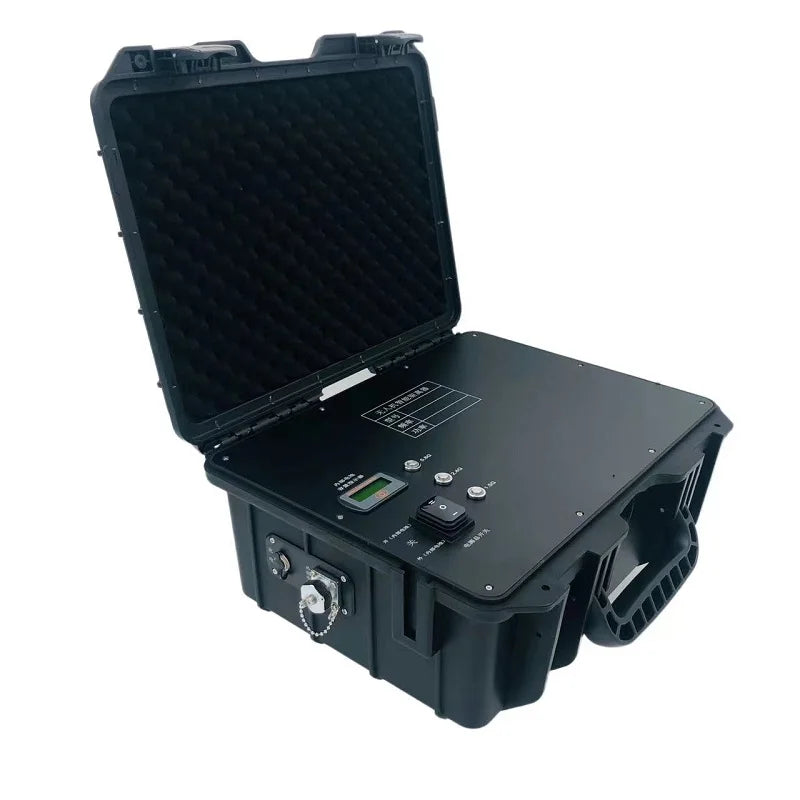

Anti Drone Device
Protect Airspace with Anti Drone Devices – This collection features handheld,...
-

Drone Antenna
Enhance your drone's signal with our premium antennas for FPV, long-range, and...
-

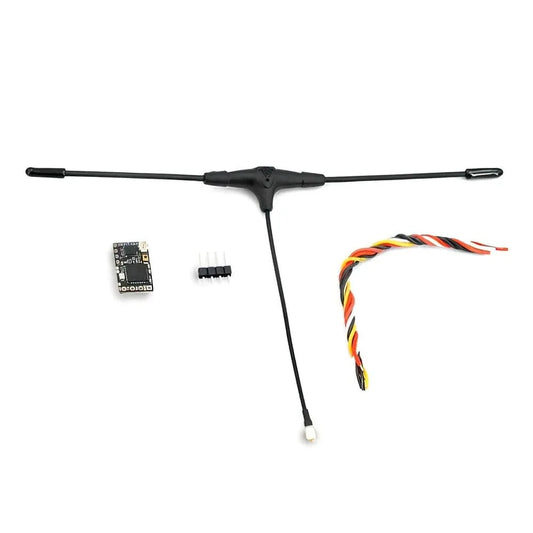
ELRS Transmitter & Receivers
Explore our ELRS Transmitters & Receivers collection, featuring ultra-low latency, long-range 2.4GHz...
-

TBS Crossfire Transmitter & Receivers
The TBS Crossfire Transmitter & Receivers collection delivers ultra-reliable long-range control for...
By Frequency Band
-

433MHz Long-Range Control & Telemetry
Enhance your FPV drone, UAV, or RC aircraft with 433MHz long-range control...
-

900MHz/868MHz Long Range System
Enhance your long-range FPV connectivity with 900MHz/868MHz systems, delivering stable signal transmission...
-

1.2GHz/1.3GHz Video Transmitter & Receiver
Discover our range of 1.2GHz and 1.3GHz FPV video transmitters and receivers,...
-
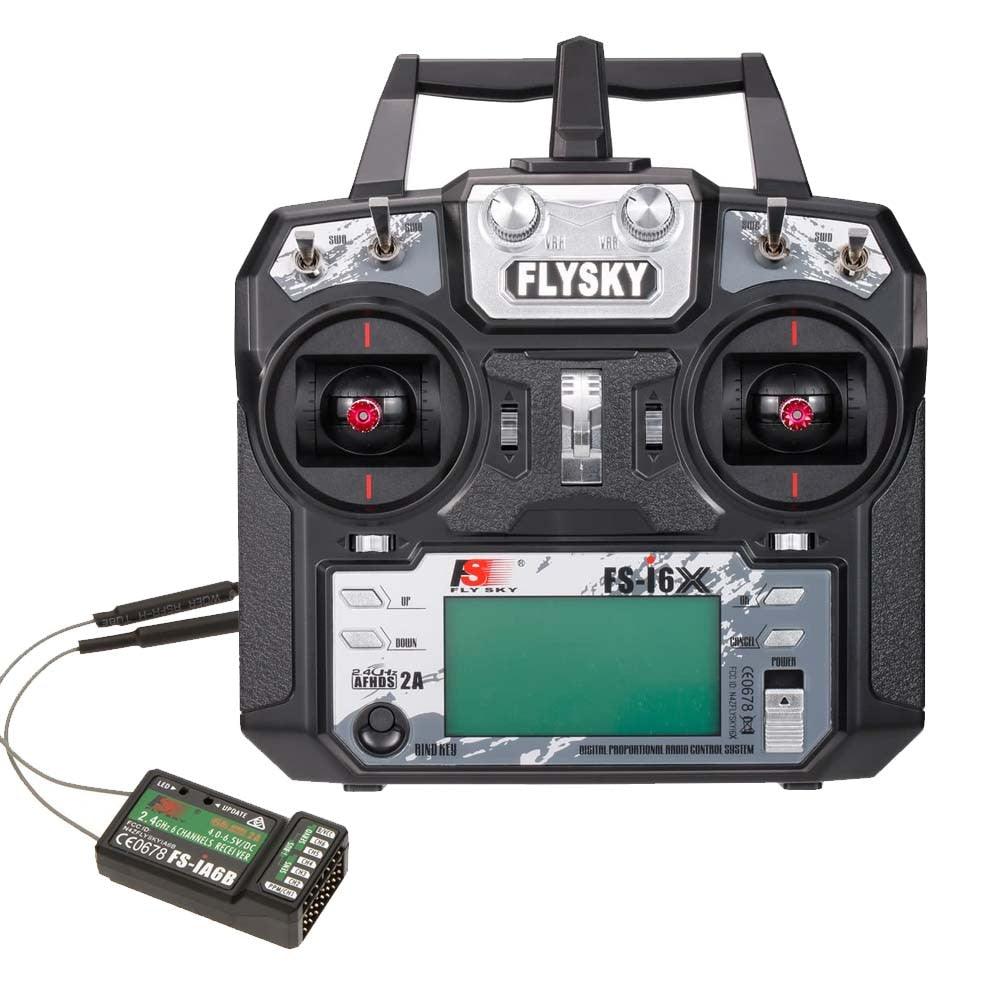

2.4GHz Transmitter & Receiver
Discover a wide selection of 2.4GHz transmitters and receivers designed for FPV...
-

5.8GHz Video Transmitter & Receiver
Upgrade your FPV system with 5.8GHz video transmitter and receiver combos, delivering...
By Radio Brand
-
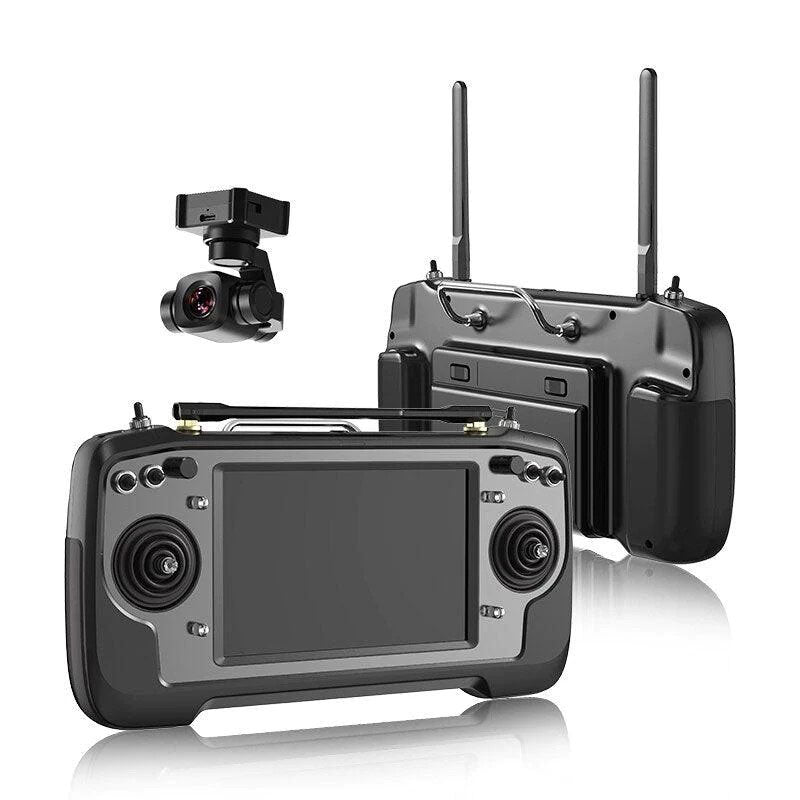

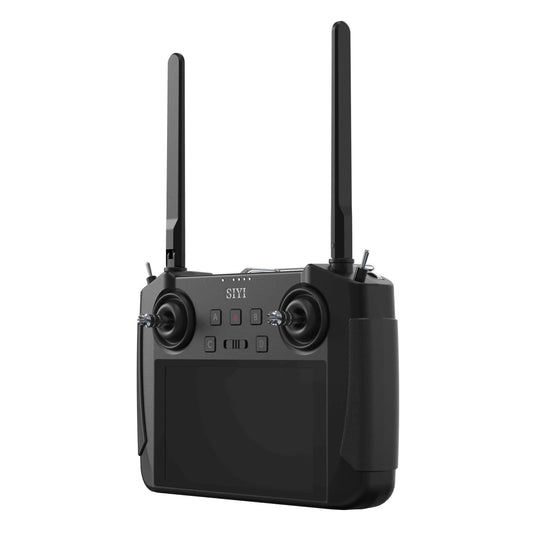
SIYI Remote Controller
SIYI is a leading brand in professional UAV ground control systems, offering...
-
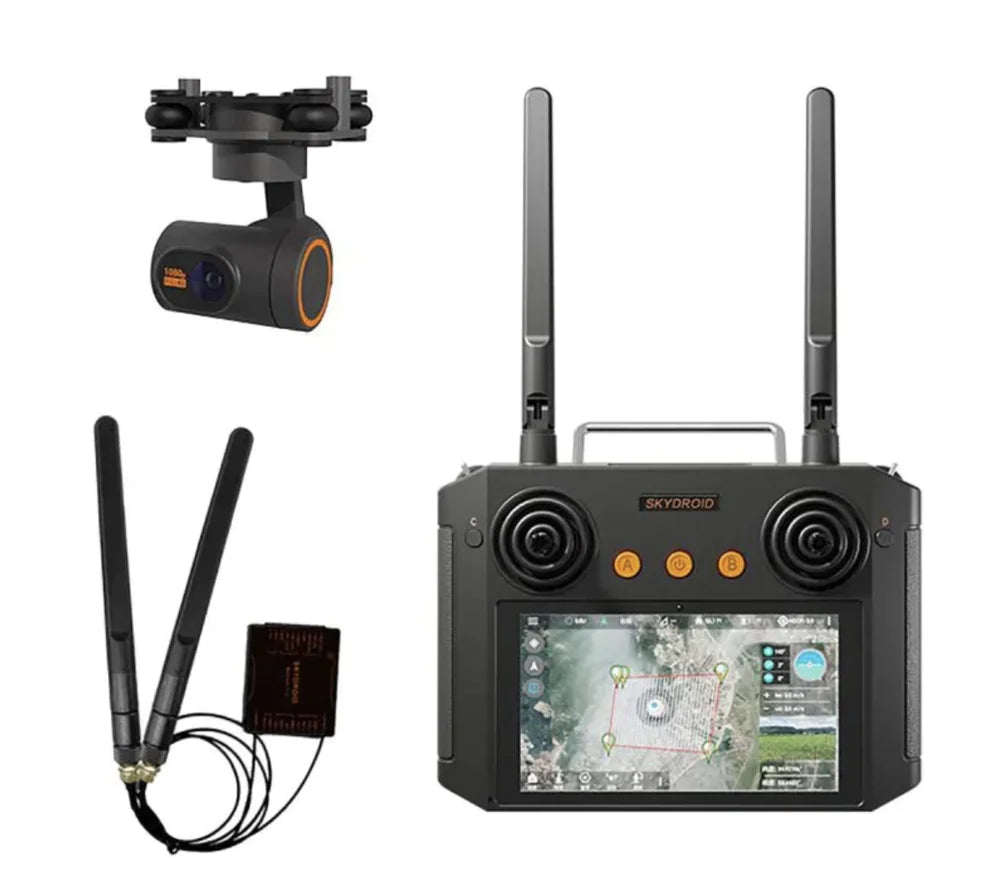

Skydroid Remote Controller
Skydroid offers professional-grade remote controllers designed for UAVs, agricultural drones, and industrial...
-
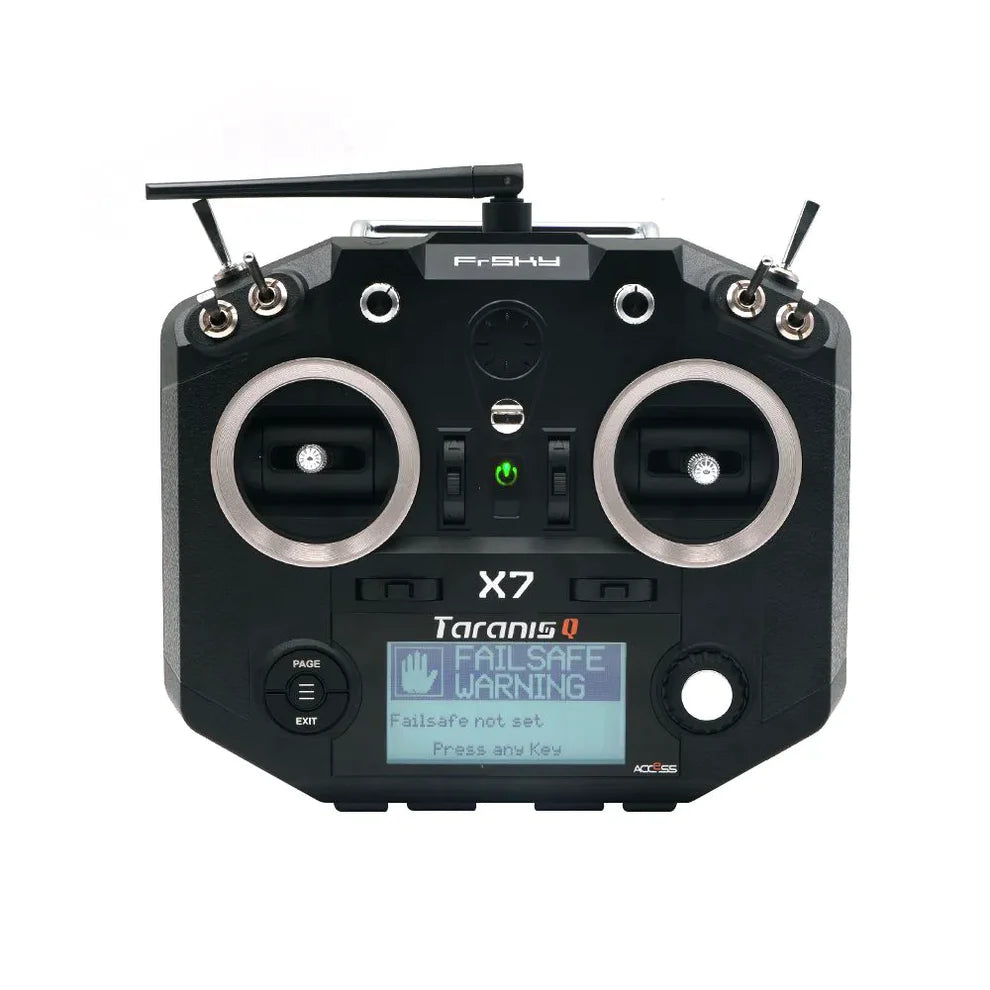

FrSky Remote Controller
FrSky remote controllers are trusted by FPV pilots and RC enthusiasts for...
-
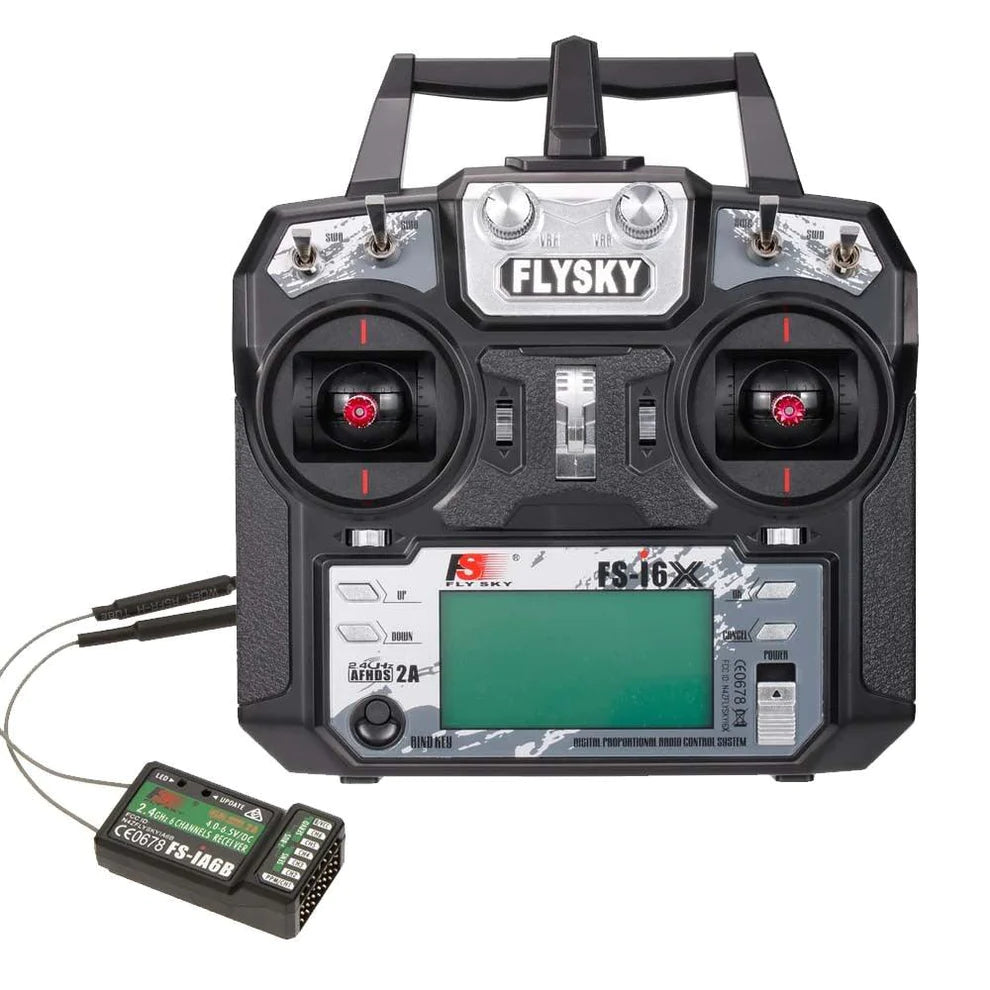

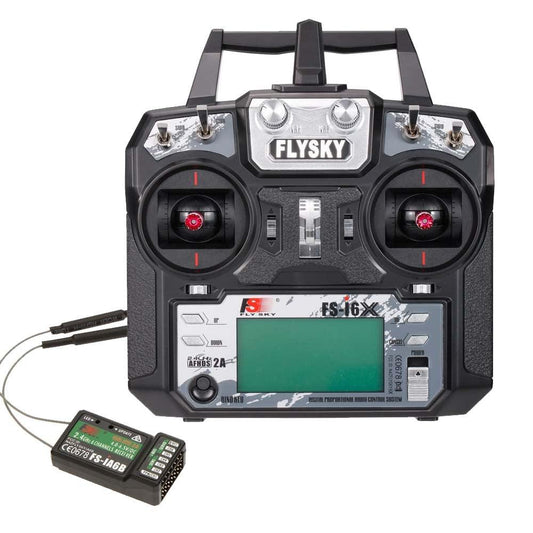
Flysky Remote Controller
FlySky is a trusted brand for RC remote controllers, offering high-performance transmitters...
-

Futaba Air Transmitter
Futaba Air Transmitters offer professional-grade control systems for RC airplanes, helicopters, and...
-

RadioMaster
The RadioMaster product collection offers top-quality radio controllers and accessories for RC...
-

Radiolink Remote Controller
Radiolink remote controllers are trusted by RC hobbyists and professionals for their...
-
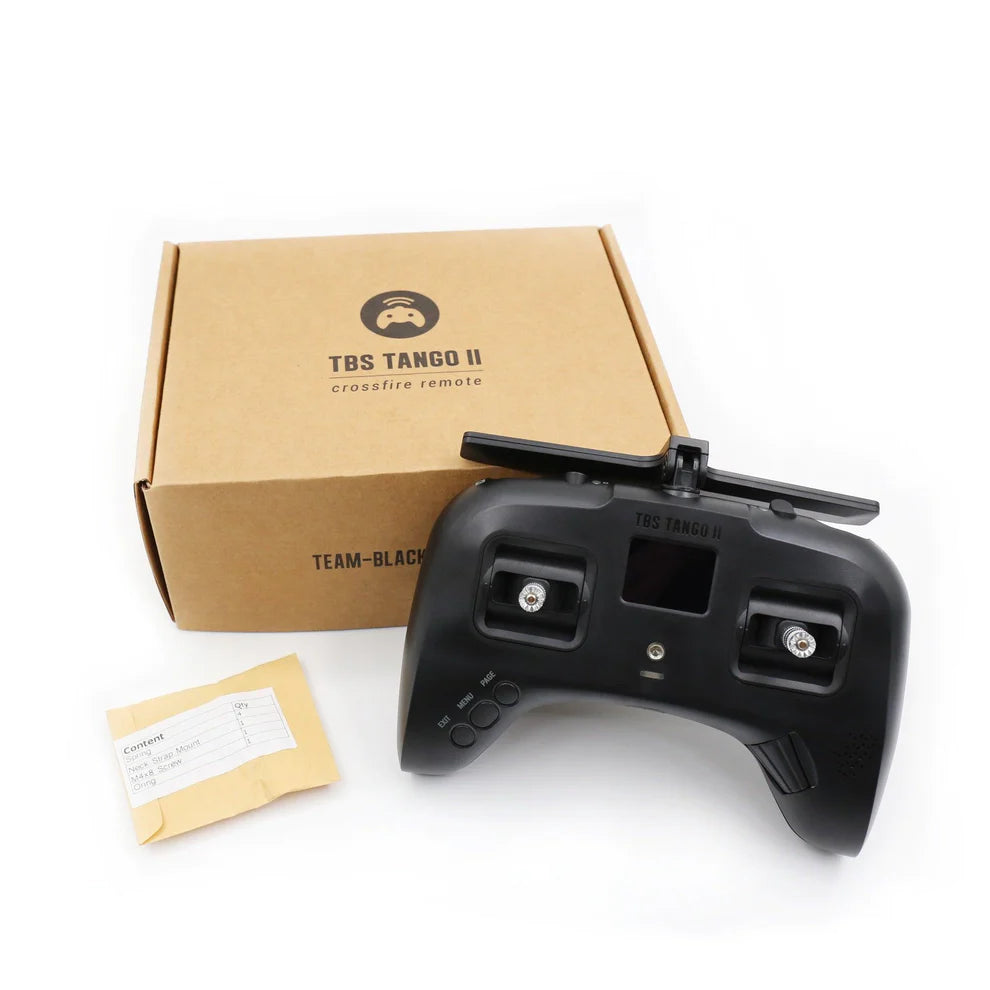

TBS Remote Controller
TBS remote controllers, including the popular Tango 2 and Mambo, are...
-
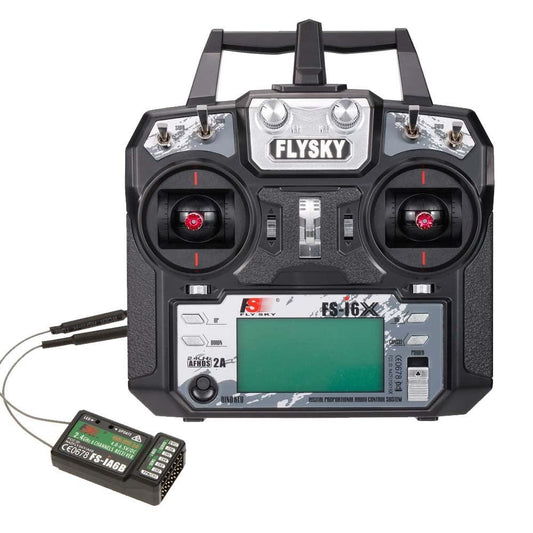
FLYSKY FS-i6x 2.4G 6CH AFHDS 2A Radio Transmitter IA6B X6B A8S R6B Fli14+ Receiver for RC Airplane Helicopter FPV Racing Drone
Regular price From $24.24 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
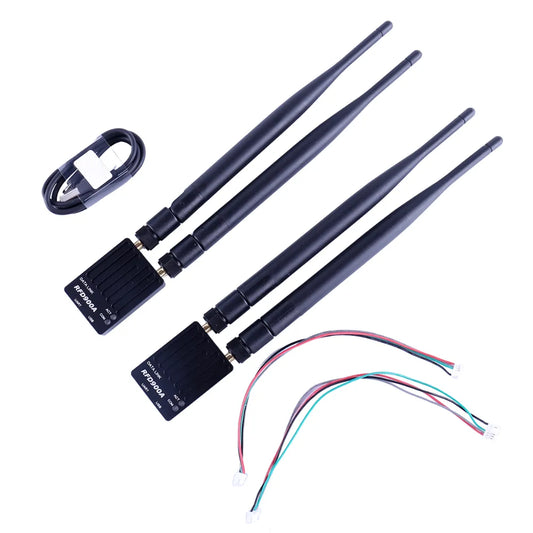
RFD900A 915Mhz 3DR Radio Telemetry Modem Module - UAV 40KM Ultra Long Range Data Link Transmission for PIX APM RC Drone Airplane
Regular price From $88.47 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
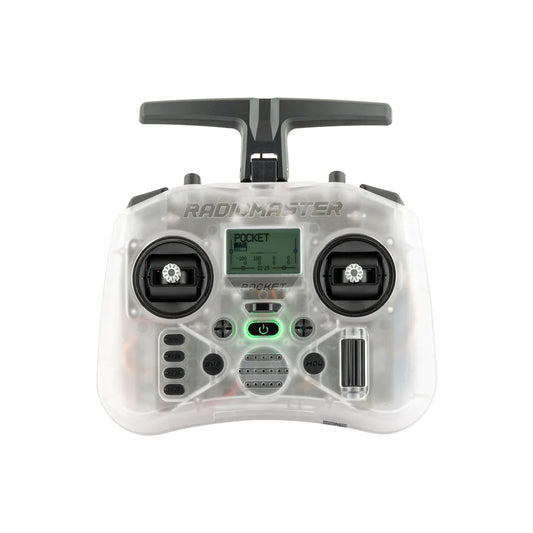
RadioMaster Pocket Radio Controller (M2) - 16Channel 2.4GHZ ExpressLRS MPM CC2500 EdgeTX System
Regular price From $99.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Futaba T16IZ Super 18CH Transmitter with R7308SB Receiver | FASSTest & S.Bus2 Compatible
Regular price From $669.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Futaba T6K V3S Transmitter - 8 Channel 2.4GHz S-FHSS/T-FHSS Radio System With R3006SB / R3008SB Receiver
Regular price From $259.99 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
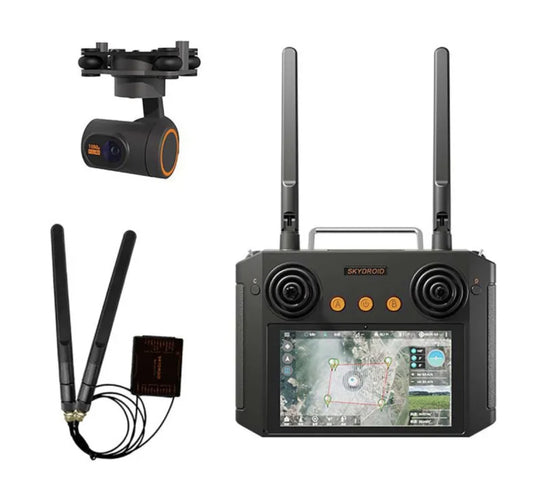
Skydroid H12 PRO Remote Control for UAV Agricultural Sprayer Drone With 10KM 2K 1080P Video Stream 3-Axis Camera
Regular price From $369.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Holybro SiK Telemetry Radio V3 - 100mW 500mW 433MH 915MHz Open-source SiK firmware Plug-n-play for Pixhawk Standard Flight Controllers
Regular price $81.73 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Futaba Attack 4YWD Transmitter - 4-Channel 2.4GHz Radio System w/Receiver
Regular price $139.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
RadioMaster TX16s Rear Case Speaker Optional Upgrade set For RadioMaster TX16S
Regular price From $10.20 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
SKYZONE 1.2GHz Diversity Receiver 4db antenna
Regular price $89.78 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
RD945 Skyzone ISM 5.8G Wireless Dual Receiver & TS832 Transmitter 5.8GHz 48CH VTX For 250MM FPV Multicopter RC Toys Part
Regular price From $28.66 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
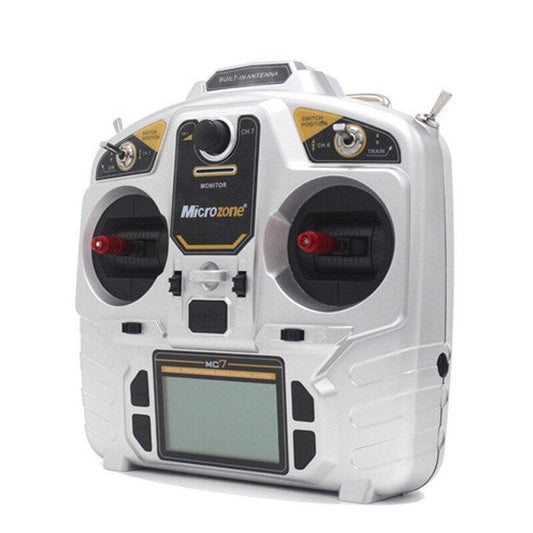
MicroZone MC7 - 2.4G Controller Transmitter With MC8RE Receiver Radio System for RC Airplane Drone multirotor Helicopter VS MC6C
Regular price From $21.67 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Skydroid H12 2.4GHz 12 Channel 1080P remote control spray drone digital image control R12 Receive Plant Protection Machine
Regular price From $50.72 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
3DR Radio Data Telemetry - 433mhz 433 1000MW 915mhz 500mw Data Telemetry TTL & USB Port For APM2.6 APM2.8 Pixhawk 2.4.8 Pixhack FPV RC Drone
Regular price From $77.17 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
SIYI UniRC 7 / 7 Pro - 2.4 & 5 GHz 40KM 7 Inch 1080P Handheld Ground Station for UAV Drone
Regular price From $199.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Jumper T20S T20 V2 - 2.4G 915MHz 1W RDC90 HALL VS-M Full Size Radio Remote Control Edgetx ELRS
Regular price From $138.94 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Original RadioMaster TX16S Parts Fit For Replacement TX16S Hall TBS Sensor Gimbals 2.4G 12CH Radio Transmitter
Regular price From $10.20 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
SIYI MK15 Mini HD Handheld Smart Controller Remote Control 15KM 1080P Low-Latency Radio System Transmitter Agriculture FPV
Regular price From $573.23 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Remote Controller For RG106 Pro/Max Drone
Regular price $49.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Flysky FS-i6X Transmitters - 2.4GHz 6CH AFHDS 2A RC Transmitter with FS-iA6B Receiver for RC Drone Airplane Helicopter FPV Remote Controller
Regular price From $26.87 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Futaba R9001SB 1Ch 920MHz System S.Bus port Air Receiver
Regular price $189.99 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FUTABA R7308SB 8 Channel 2.4GHz FASSTest High Gain Antenna S.BUS Receiver
Regular price $182.96 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Skydroid UVC Single Control Receiver - OTG 5.8G 150CH Channel FPV Receiver Video Transmission Downlink Audio For Android phone
Regular price $39.86 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FrSky V8FR-II 2.4Ghz 8CH ACCST Receiver
Regular price $35.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
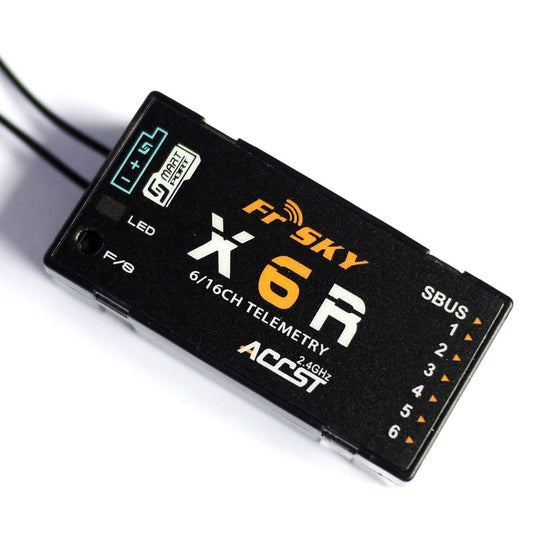
FrSky RX6R Receiver - 6 PWM and 16 Channels Sbus outport with redundancy function
Regular price $50.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
RadioMaster RP1 V2 ExpressLRS 2.4ghz Nano Receiver - With Built-in TCXO Fit For Whoops, Drone, Fixed-Wing Aircraft
Regular price $32.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
TBS Crossfire Tx Lite - Team BlackSheep 868MHZ / 915MHZ 1.1W 3.2W 76g Long Range R/C Transmitter
Regular price $179.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Holybro SiK Telemetry Radio V3 - 100mW 433MH 915MHz Open-source SiK firmware Plug-n-play for Pixhawk Standard Flight Controller
Regular price $83.24 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
3DR Radio V5 Telemetry - 433Mhz 915Mhz 100MW/500MW Air and Ground Data Transmit Module with OTG cables for APM 2.8 /Pixhawk 2.4.8
Regular price From $15.25 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FLYWOO TBS Crossfire Nano Rx
Regular price $39.25 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
FrSky X6R 6ch 16Ch S.BUS ACCST Telemetry Receiver With Smart Port
Regular price $37.71 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
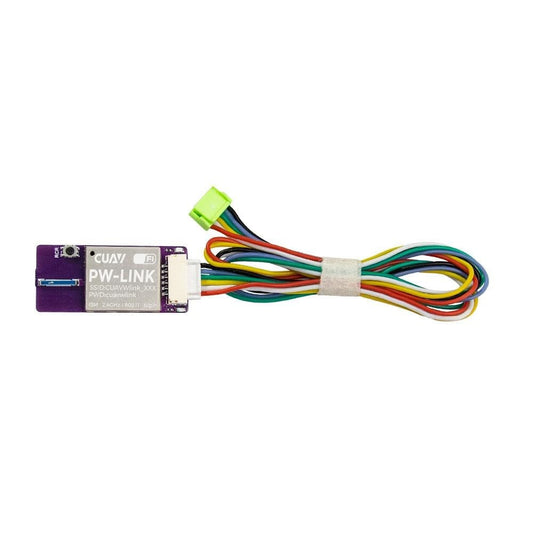
CUAV PW-LINK Wifi Telemetry Module - Wifi Data Transmission for PIX FPV Telemetry PIXHACK PIXHAWK Flight Controller
Regular price $46.73 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Goggles Receiver - 1Set ImmersionRC 5.8G RapidFire Analog PLUS Goggles Dual Receiver Module For FatShark RFIRE01 FPV RC Drone Multicopter Parts
Regular price $298.07 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Futaba WSC-1 Wireless USB Simulator Control Link for RealFlight (S-FHSS Compatible)
Regular price $79.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
Futaba 10J Transmitter - 10 Channel 2.4GHz S-FHSS T-FHSS Radio Controller with R3008SB
Regular price From $389.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
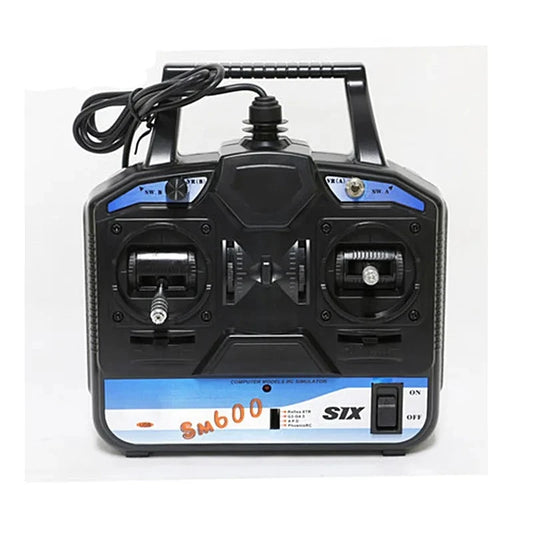
FlySky SM600 6 Channel RC Flight Simulator for RC Plane,Helicopter , Drone Training
Regular price $45.92 USDRegular priceUnit price per