-
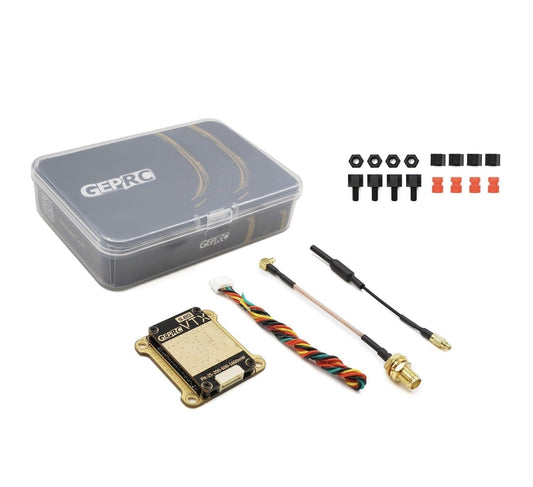
GEPRC RAD VTX - 5.8G 1.6W 40CH PITMode 25mW 200mW 600mW 1600mW Adjustable Video Transmitter 30X30mm For RC FPV Quadcopter Drone
Regular price $78.00 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
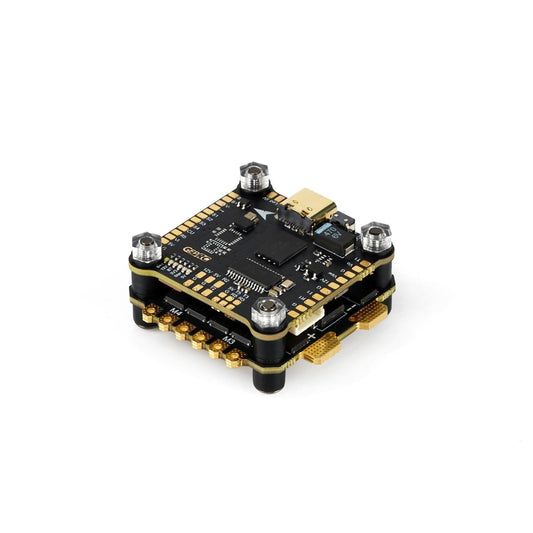
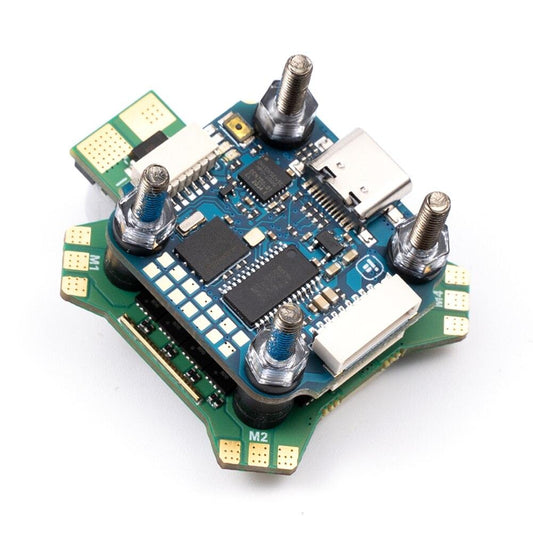
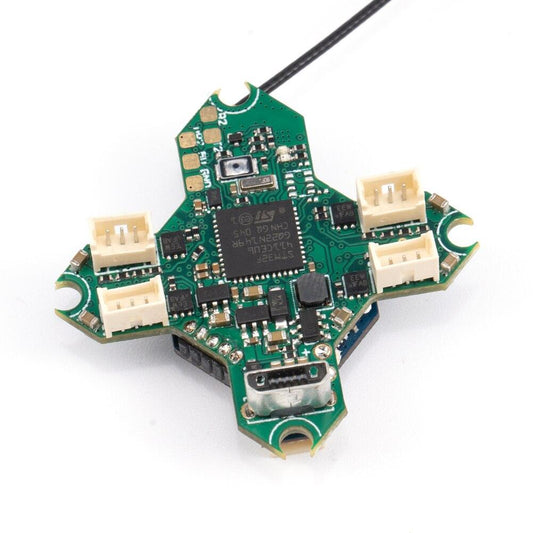
GEPRC SPAN F722-BT-HD V2 Stack - Flight Controller Stack F7 BL32 50A 96K 4IN1 ESC SUPPORT BLUETOOTH PARAMETER TUNING
Regular price From $112.68 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
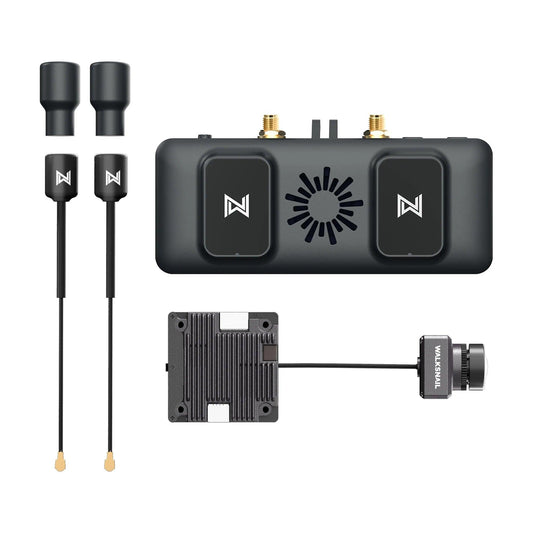
Walksnail Avatar VRX 1080P 60FPS 4KM Distance with Avatar 1S Kit Avatar HD Micro Kit for FPV Freestyle Drones
Regular price From $345.83 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
iFlight SucceX Micro Force 5.8GHz PIT/25/100/200mW/300mW VTX Adjustable with IPEX (UFL) connector for FPV part
Regular price $42.33 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
iFlight SucceX- RACE VTX 25mW Non-adjustable with MMXC connector for FPV parts
Regular price From $46.02 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
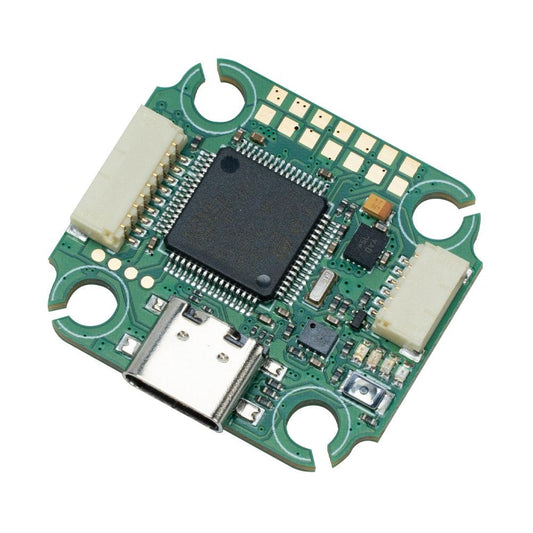
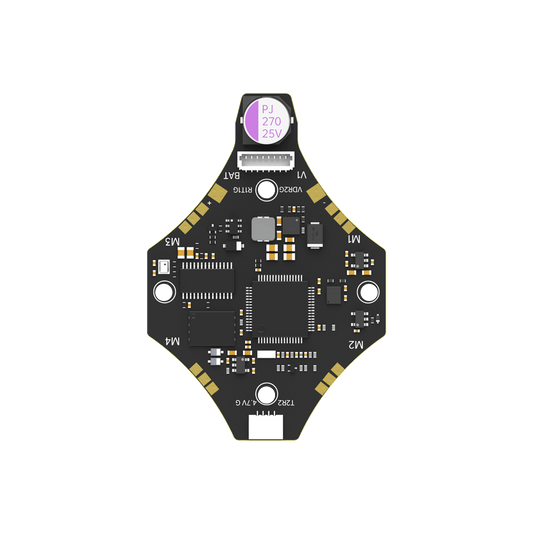
iFlight BLITZ Mini F7 V1.1 Flight Controller for FPV
Regular price $91.02 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
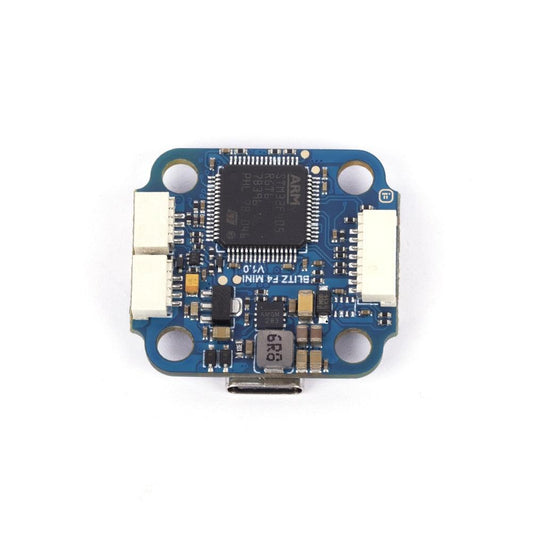
iFlight BLITZ Mini F4 Flight Controller with 20*20mm/φ4 mounting hole for FPV
Regular price $71.89 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
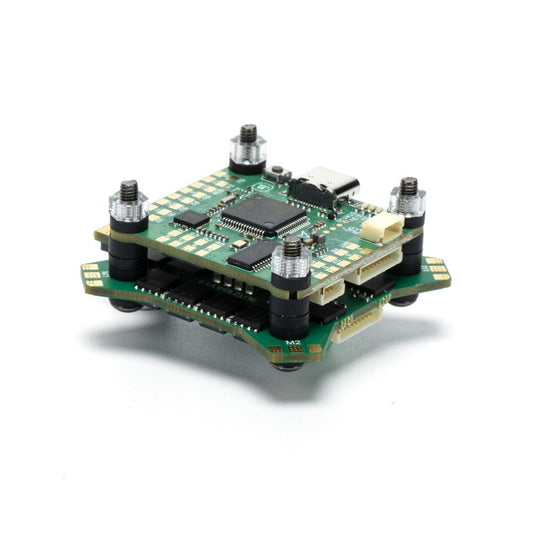
iFlight BLITZ Mini F4 Stack with BLITZ Mini F4 Flight Controller / BLITZ Mini E55S 4-IN-1 2-6S ESC for FPV
Regular price $136.18 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
iFlight BLITZ E80 2-8S 80A Single ESC for FPV parts
Regular price From $90.48 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
iFlight BLITZ E80 4-IN-1 80A Pro ESC (G2)with 35x35mm Mounting Holes for FPV
Regular price $337.94 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
iFlight BLITZ E55 Single 55A 2-6S ESC for FPV
Regular price From $41.95 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
iFlight SucceX-E Mini F7 55A Stack with Succex-E mini F7 2-6S V1.4 Flight Controller / BLITZ Mini E55S 4-IN-1 ESC for FPV parts
Regular price $148.01 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
iFlight SucceX-E Mini F7 V1.4 2-6S STM32F22RET6 216MHz Flight Controller(MPU6000)with 20*20mm hole for FPV part
Regular price $63.73 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
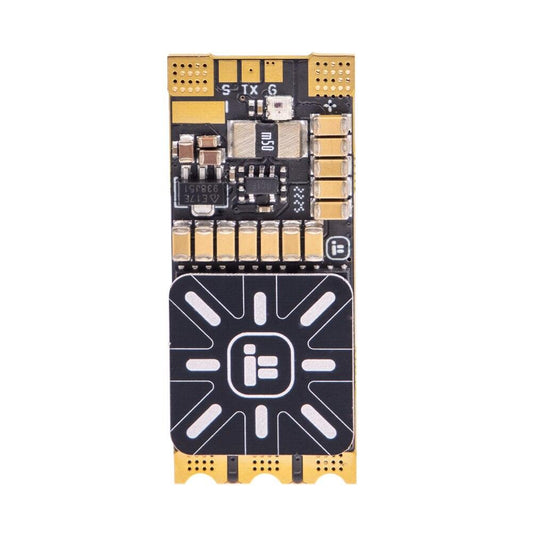
iFlight BLITZ F411 1S 5A Whoop AIO Board Built-in ELRS 2.4G Receiver (BMI270) for FPV
Regular price $88.71 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
iFlight Defender 25 F7 AIO with 25.5*25.5mm Mounting holes for FPV parts
Regular price From $184.22 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
3pcs iFlight Led Lights for XL5 v5 / Nazgul5 / Chimera7 FPV drone part
Regular price $17.33 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
2pcs iFlight Led Lights for Protek25 / Protek35 / Protek25 Pusher FPV drone part
Regular price $9.72 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
iFlight SucceX Mini Force 5.8GHz 600mW VTX Adjustable with MMCX Connector for FPV part
Regular price $48.79 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
iFlight SucceX Mini Force 5.8GHz 600mW VTX Adjustable with MMCX Connector for FPV part
Regular price $48.79 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
iFlight FPV M8Q-5883-GPS Module V2.0 integrate Compass module QMC5883L Built-in TCXO crystal and farad capacitor for FPV drone
Regular price $54.28 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
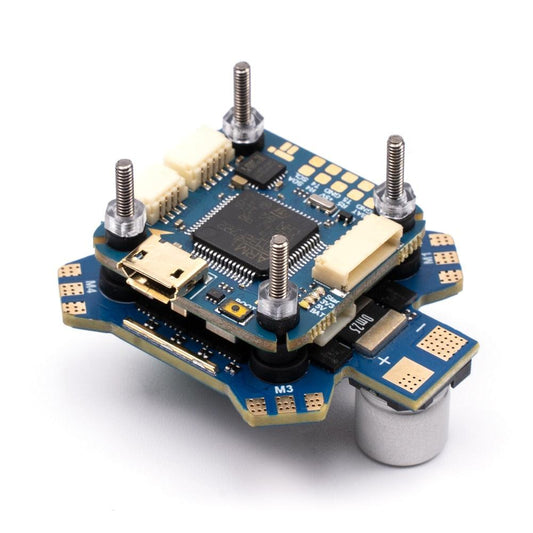
iFlight BLITZ F7 55A 2-6S Stack - with BLITZ F7 V1.1 Flight Controller / BLITZ E55 4-IN-1 2-6S ESC for FPV
Regular price $162.55 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
4pcs iFlight Programmable RGB 9 LED lights - 75mm / 116mm length with Prop Ducts for BumbleBee Green Hornet FPV CineWhoop parts
Regular price From $23.79 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
iFlight 5.8G SucceX Micro V2 VTX (M3) Switchable PIT/25/100/200mW Video Transmitter with IPEX (UFL) Connector for FPV drone part
Regular price $28.41 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
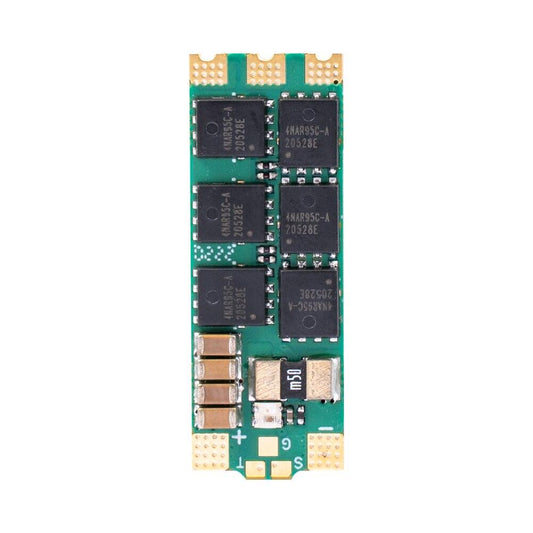
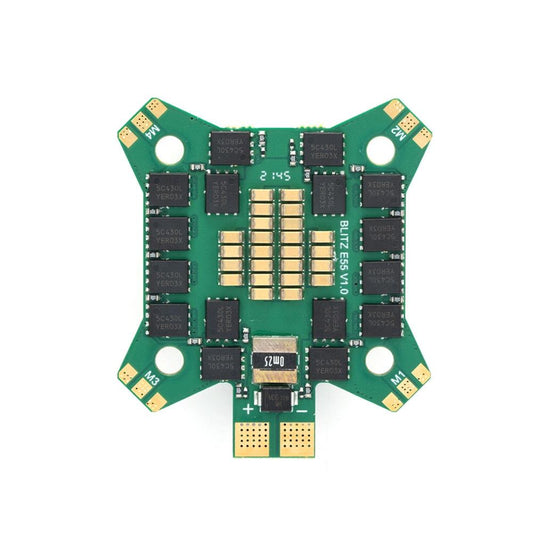
iFlight BLITZ E55 4-IN-1 2-6S ESC(G2)support DShot150/300/600/MultiShot/OneShot for FPV
Regular price $90.48 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
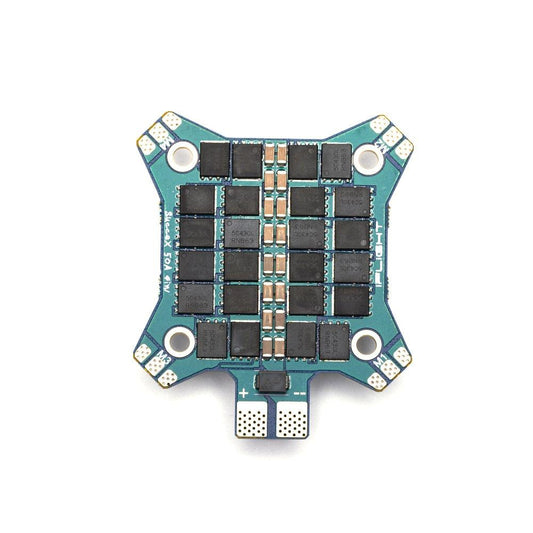
iFlight SucceX 50A 2-6S BLHeli_32 Dshot600 4-in-1 ESC (F051) for FPV part
Regular price $136.18 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
iFlight BLITZ F7 V1.1 Flight Controller for FPV
Regular price $77.39 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
iFlight BLITZ Mini E55 4-IN-1 2-6S BLHeli 32 ESC - with 20*20mm/Φ4mm Mounting Holes for FPV
Regular price $117.58 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
iFlight Whoop F4 V1.1 AIO Board - (BMI270) with 25.5*25.5mm Mounting holes for FPV
Regular price $99.10 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
iFlight BLITZ F7 45A 2-6S Stack - with BLITZ F7 V1.1 Flight Controller / BLITZ E45S 4-IN-1 ESC / BLITZ 1.6W VTX for FPV
Regular price From $171.14 USDRegular priceUnit price per -
iFlight BLITZ Mini F7 Stack - with BLITZ Mini F7 V1.1 Flight Controller / BLITZ Mini E55 4-IN-1 2-6S ESC for FPV parts
Regular price $150.86 USDRegular priceUnit price per